
9414348220
contact usAcne
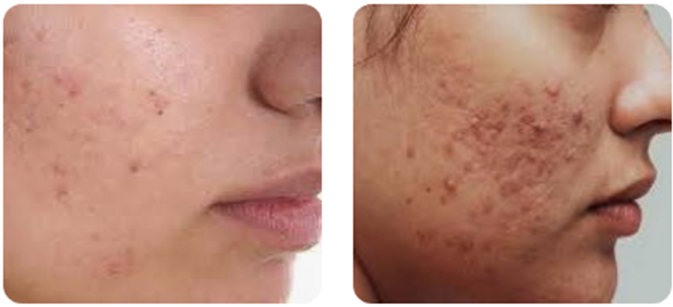
What is acne?
It is caused when blocked skin follicles from a plug caused by oil from glands, bacteria, and dead cells clump together and swell.
Alopecia Areata
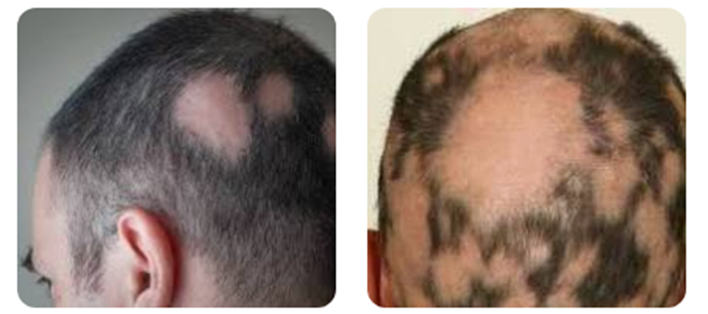
What is alopecia areata?
It is a condition that attacks your hair follicles (they make hair). In most cases, hair falls out in small, round patches.
Atopic Dermatitis
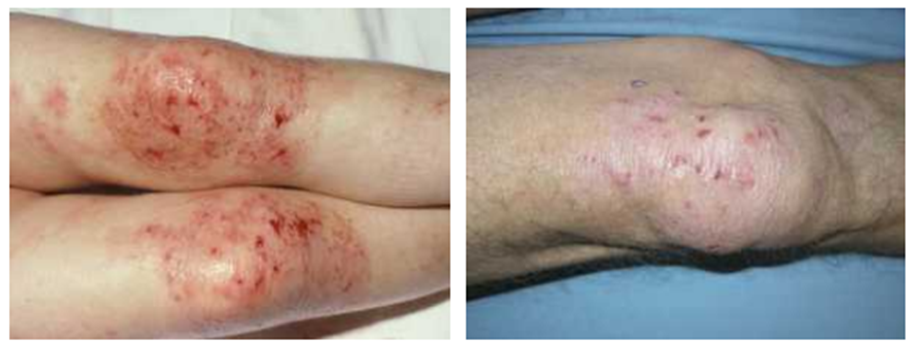
What is atopic dermatitis?
It is a skin disease causing much itchiness. Scratching leads to redness, swelling, cracking, weeping clear fluid, crusting, and scaling.
Epidermolysis Bullosa
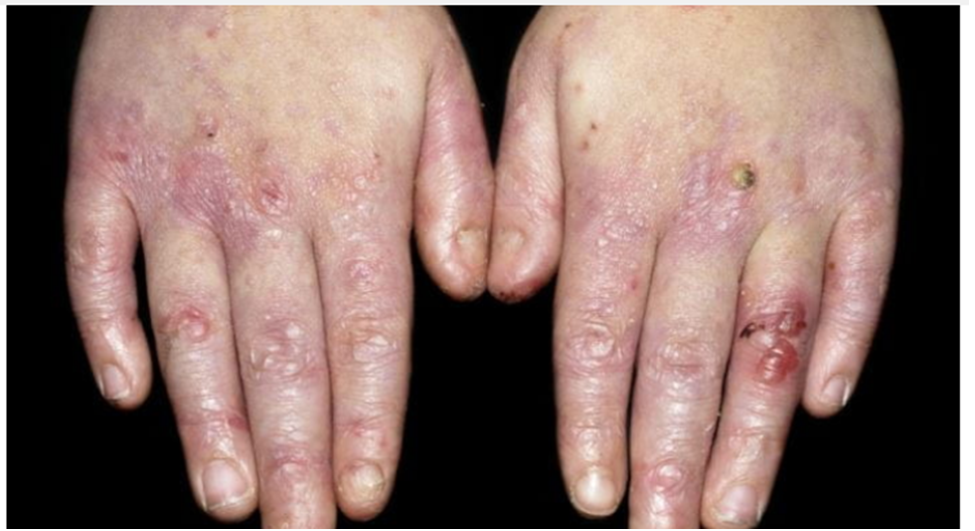
What is epidermolysis bullosa?
It is a group of diseases causing painful blisters to form on the skin. These blisters can cause problems if they become infected.
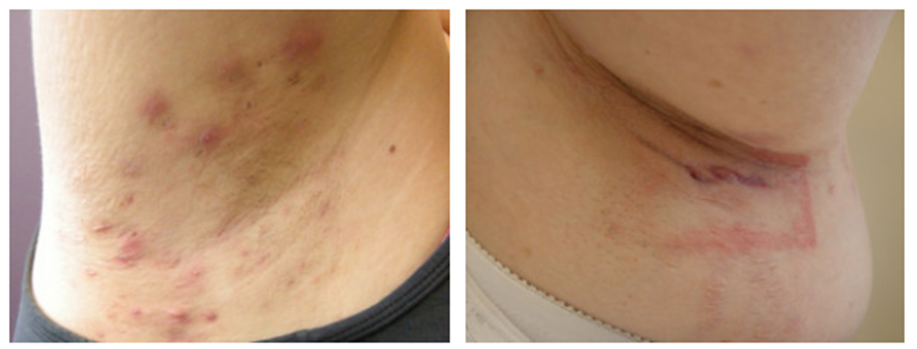
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS)
Hidradenitis suppurativa (also known as acne inversa) is a chronic, noncontagious, inflammatory condition characterized by pimple-like bumps or boils and tunnels or tracts on and under the skin.
Ichthyosis
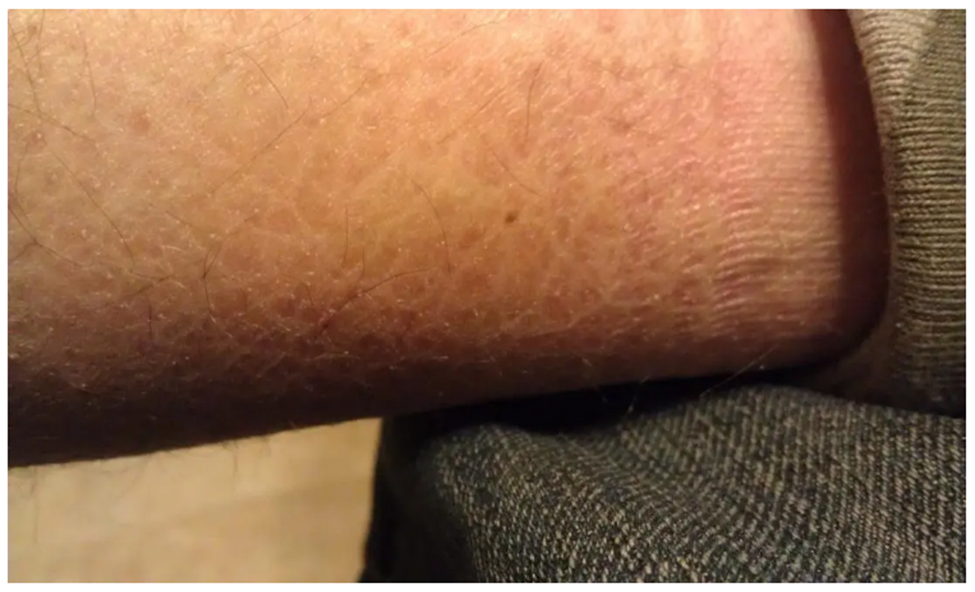
What is ichthyosis?
It is a disorder that causes dry, thickened skin that may look similar to fish scales.
Pachyonychia Congenita
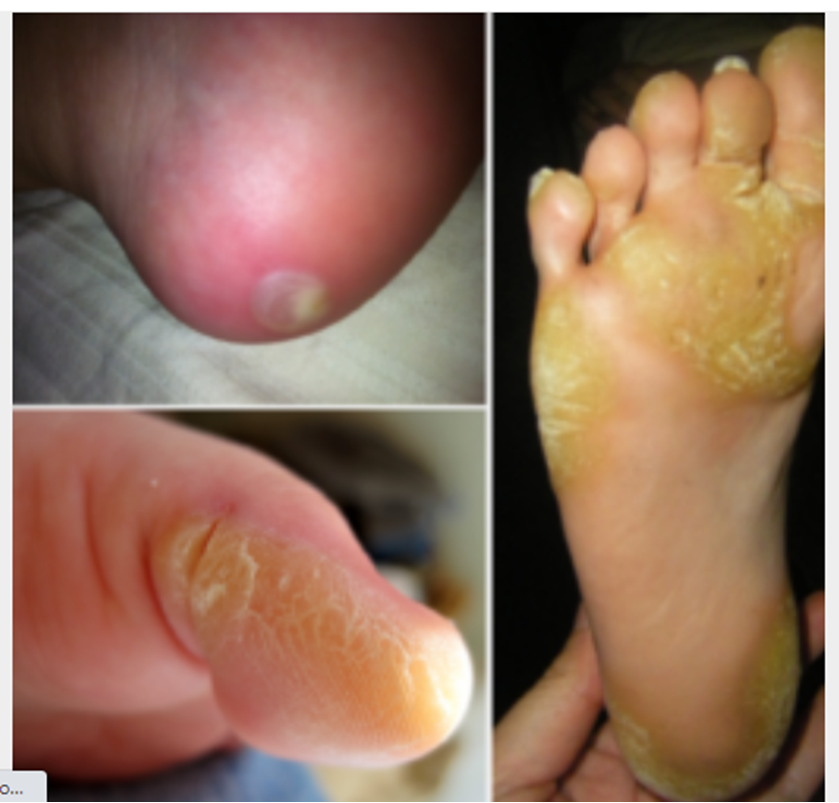
What is pachyonychia congenita?
It is a rare disorder causing thick nails and painful calluses on the bottoms of the feet and other symptoms.
Pemphigus
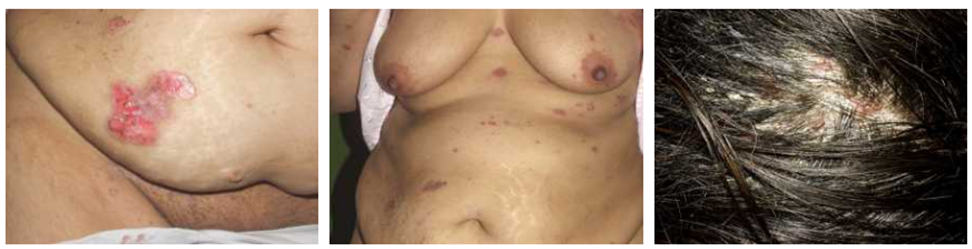
What is pemphigus?
It is a disease where the immune system attacks healthy cells in the top layer of skin, resulting in blisters.
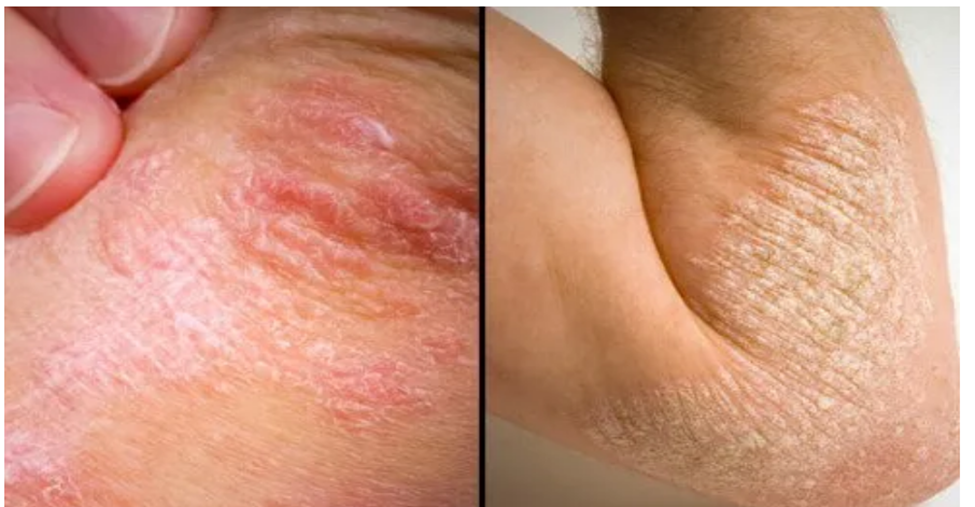
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin disease that causes red, scaly skin that may feel painful, swollen, or hot. Learn more about the types and what causes psoriasis.
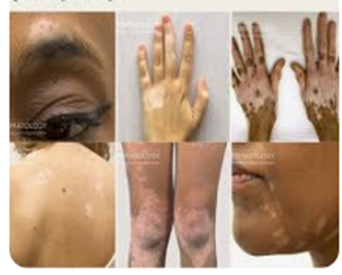
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a disorder that causes patches of skin to become white. It happens because cells that make color in your skin are destroyed.
Raynaud's Phenomenon
What is Raynaud's phenomenon?
It is a disease that affects blood vessels. It causes your body to not send enough blood to the hands and feet for a period of time.
Rosacea
What is rosacea?
It is a long-term disease that causes reddened skin and pimples, usually on the face. It can also make the skin thicker and cause eye problems.
Scleroderma
Scleroderma causes areas of tight, hard skin, but can also harm your blood vessels and organs. Learn the causes and treatments of this skin disease.
Human hair is a diverged one. It come in different textures and different colour. Hair is a significant feature of human appearance, serving both functional and aesthetic purposes. It consists of a protein called keratin, which is produced in hair follicles embedded in the skin.

1. Alopecia Areata:
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss in round patches. It can progress to more extensive hair loss on the scalp or body. The exact cause is not fully understood, but genetics and environmental triggers are believed to contribute.
2. Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness):
This hereditary form of hair loss is most common in men and women. It's characterized by gradual hair thinning, typically starting at the hairline or crown. Androgens, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a role in shrinking hair follicles over time.
3. Tinea Capitis (Ringworm of the Scalp):
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection that affects the scalp, causing red, scaly patches and hair breakage. It's common in children and is highly contagious.
4. Telogen Effluvium:
This temporary hair shedding condition is often triggered by stress, illness, surgery, or hormonal changes. It disrupts the hair growth cycle, causing more hair follicles to enter the resting phase and eventually shed.
5. Trichotillomania:
Trichotillomania is a psychological disorder characterized by the urge to pull out one's hair, often as a coping mechanism. This leads to patchy hair loss and broken hairs, usually in easily accessible areas.
6. Folliculitis:
Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicles, commonly caused by bacterial or fungal infections. It can result in red, pimple-like bumps around hair follicles, sometimes leading to hair loss.
7. Seborrheic Dermatitis:
This chronic skin condition causes red, itchy, and flaky patches on the scalp, known as dandruff. It can lead to temporary hair loss due to irritation and inflammation of hair follicles.
8. Scarring Alopecia (Cicatricial Alopecia):
Scarring alopecia involves inflammation that permanently damages hair follicles, replacing them with scar tissue. It can result from various causes, including autoimmune diseases or infections.
9. Lichen Planopilaris:
This inflammatory condition affects hair follicles and can cause itching, redness, and scaly patches on the scalp. Over time, it can lead to permanent hair loss.
10. Psoriasis:
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that can extend to the scalp, causing red, scaly patches. In severe cases, it can lead to hair loss due to the damage inflicted on hair follicles.
11. Alopecia Universalis and Totalis:
These conditions are severe forms of alopecia areata, resulting in total hair loss on the scalp and body (alopecia universalis) or only on the scalp (alopecia totalis).
Some of the other diseases include:
Conclusion:
Understanding common hair diseases is essential for recognizing their signs, seeking timely treatment, and managing their effects on hair health and appearance. Many of these conditions have a significant impact on self-esteem and overall well-being. If you suspect you have a hair disease, consulting Dr Mirza's Homoeo is recommended for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
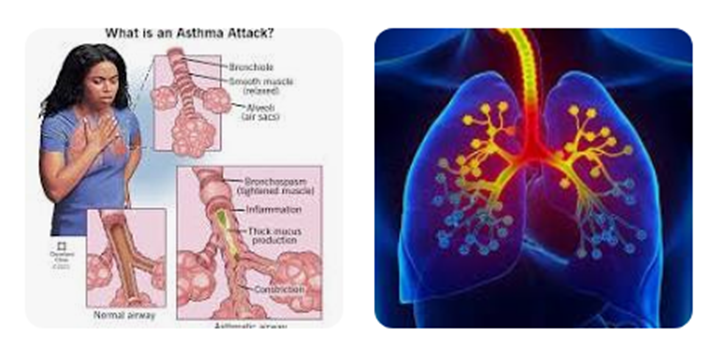
Asthma
Asthma affects 25 million people in the United States. People with a family history of asthma, respiratory allergies, or severe childhood respiratory illness are at a higher risk of developing asthma.
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease that causes breathing problems when the airways become narrowed by inflammation or blocked by mucus. The condition's severity varies from person to person, but most people take daily preventive medication to control their symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Symptoms:-
Asthma can have several symptoms, including:
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)is an umbrella term used to describe two primary types of obstructive lung disease that used to be classified separately: emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
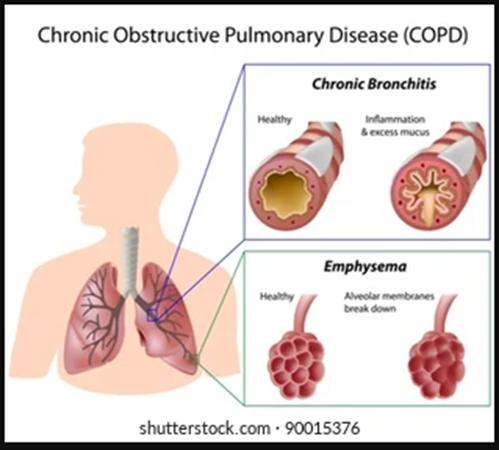
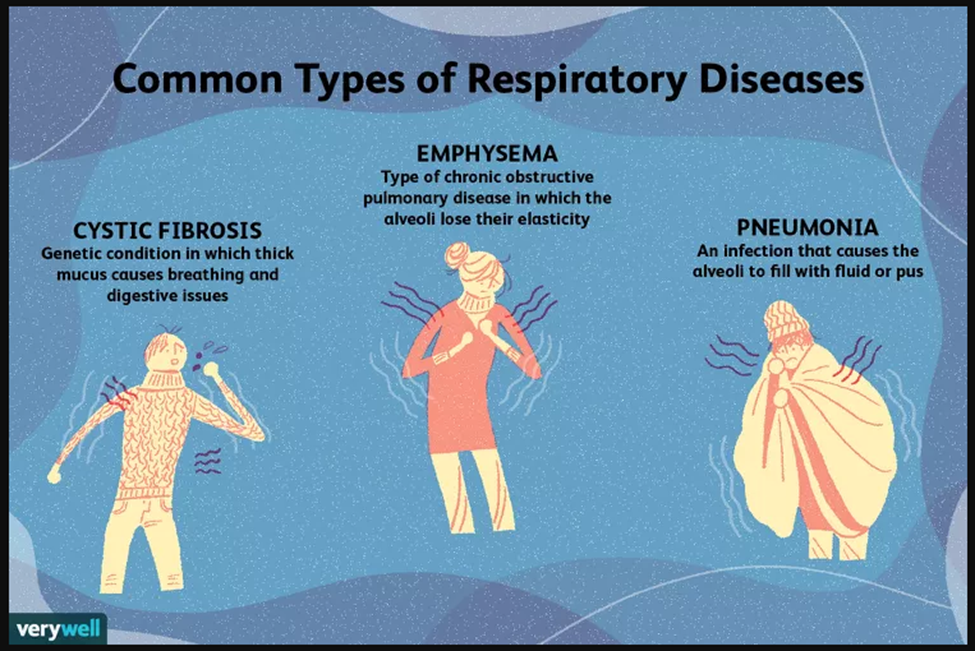
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic condition that affects about 35,000 people in the United States. It can cause both breathing and digestive problems because the disease makes the mucus in the body very thick.
While the disease can involve several organs, it tends to cause specific problems in the lungs, such as blockages from thick mucus that trap harmful bacteria and lead to infections.
Symptoms:-
Since cystic fibrosis can affect many parts of the body, a wide range of symptoms can develop, such as:
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, ranking third in the United States with more than 218,000 people affected. It can develop as either small cell lung cancer or non-small cell lung cancer. The latter is the more common of the two.
Cigarette smoking - both direct and secondhand - is one of the biggest risk factors for lung cancer.
Symptoms:-
Lung cancer can develop gradually and often with no symptoms. When it does appear, symptoms may include :-
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosisis a bacterial lung disease caused byMycobacterium tuberculosis. More than 1.8 billion people around the world have tuberculosis, but the disease is only considered active in 10 million of them.
People with strong immune systems sometimes carry an inactive form of the disease, called latent tuberculosis. In people with weaker immune systems, the bacteria attacks lung tissue. It can also spread and cause damage to other parts of the body.
Symptoms
Many respiratory diseases share symptoms, such as long-term cough. Certain symptoms are specific to one disease or another. For example, night sweats tend to occur in people with tuberculosis.
Other tuberculosis symptoms include:
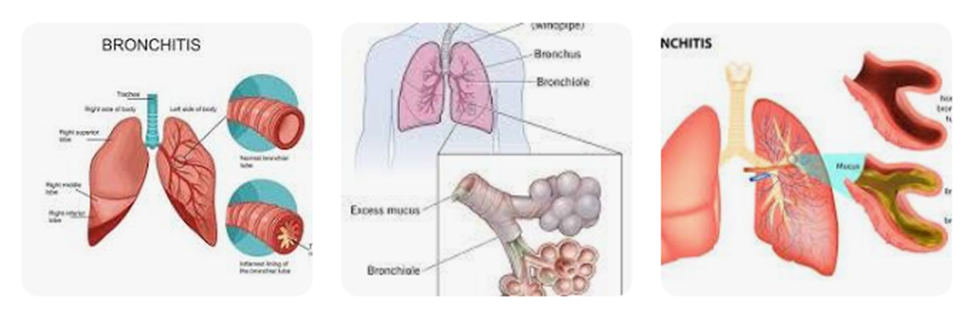
Bronchitis
Bronchitis is a condition that develops when the windpipe (bronchial tube) gets irritated or inflamed. In response to the inflammation, the lining of the bronchial tube may make too much mucus as it tries to coat the area. The mucus can make it difficult to breathe.
Inflammation can also cause swelling of the airway. This will cause it to narrow and make it harder to breathe. In acute bronchitis, the inflammation is usually caused by an infection that will get better in a few days to several weeks.
Symptoms
Chronic bronchitis falls under the umbrella of COPD. Acute bronchitis is not considered COPD, but it shares symptoms with the chronic form of the disease. These symptoms include:
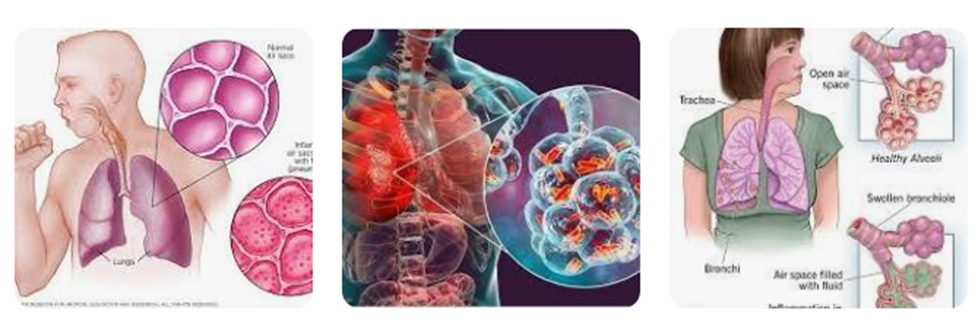
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a generic diagnosis. Even though there are different types of pneumonia, the way that the condition affects the lungs is similar in each one.
With pneumonia, a virus, bacteria, or another infectious agent causes the tiny air sacs in the lungs (alveoli) to fill with fluid or pus. These air sacs are what help exchange oxygen and other gases between the air that is breathed in and the blood. When these sacs are filled with fluid, the body's ability to exchange gases is reduced.
The several types of pneumonia are:
Symptoms:-
In some types of pneumonia, such as walking pneumonia, the symptoms can be mild and not affect daily activities. However, the symptoms of pneumonia can be severe and, in some cases, will require hospitalization.
Common symptoms of pneumonia are:
Diseases of Neonates and Children younger than five years
Neonatal infection

Diseases of older children


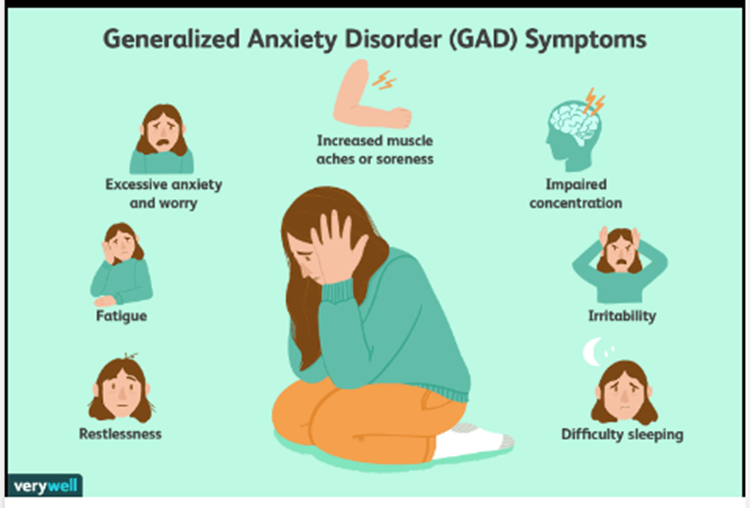
Anxiety disorders
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health disorders that includes:
Untreated, anxiety disorders can lead to significant impairment on people's daily lives.
Behavioural and emotional disorders in children
Common behaviour disorders in children include:
Treatment for these mental health disorders can include therapy, education and medication.
Bipolar affective disorder
Bipolar affective disorder is a type of mood disorder, previously referred to as "manic depression". A person with bipolar disorder experiences episodes of mania (elation) and depression. The person may or may not experience psychotic symptoms. The exact cause is unknown, but a genetic predisposition has been clearly established. Environmental stressors can also trigger episodes of this mental illness.
Depression
Depression is a mood disorder characterised by lowering of mood, loss of interest and enjoyment, and reduced energy. It is not just feeling sad. There are different types and symptoms of depression. There are varying levels of severity and symptoms related to depression. Symptoms of depression can lead to increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviours.

Dissociation and dissociative disorders
Dissociation is a mental process where a person disconnects from their thoughts, feelings, memories or sense of identity. Dissociative disorders include dissociative amnesia, depersonalisation disorder and dissociative identity disorder.

Eating disorders
Eating disorders include anorexia, bulimia nervosa and other binge eating disorders. Eating disorders can affect people of all ages and genders, and can have serious psychological and physical consequences.
Obsessive compulsive disorder
Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) is an anxiety disorder. Obsessions are recurrent thoughts, images or impulses that are intrusive and unwanted. Compulsions are time-consuming and distressing repetitive rituals.
Treatments include cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) and medications.

Paranoia
Paranoia is the irrational and persistent feeling that people are 'out to get you'. Paranoia may be a symptom of conditions including paranoid personality disorder, delusional (paranoid) disorder and schizophrenia.
Treatment for paranoia includes medications and psychological support.

Post-traumatic stress disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop as a response to people who have experienced any traumatic event. This can be a car or other serious accident, physical or sexual assault, war-related events or torture, or natural disasters such as bushfires or floods.

Psychosis
People affected by psychosis can experience delusions, hallucinations and confused thinking. Psychosis can occur in a number of mental illnesses, including drug-induced psychosis, schizophrenia and mood disorders. Medication and psychological support can relieve, or even eliminate, psychotic symptoms.

Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a complex psychotic disorder characterised by disruptions to thinking and emotions, and a distorted perception of reality. Symptoms of schizophrenia vary widely but may include hallucinations, delusions, thought disorder, social withdrawal, lack of motivation and impaired thinking and memory.
People with schizophrenia have a high risk of suicide. Schizophrenia is not a split personality.

Most Common Urology Diseases
The phrase "urologic disorders" refers to a wide range of ailments involving the filtration and removal of urine from the body. Men, women, and children of all ages can be affected by these disorders. These illnesses affect only certain areas of the body. They affect the female urinary tract. They affect the urinary tract or reproductive organs in men.
A few of the most common urology diseases include :
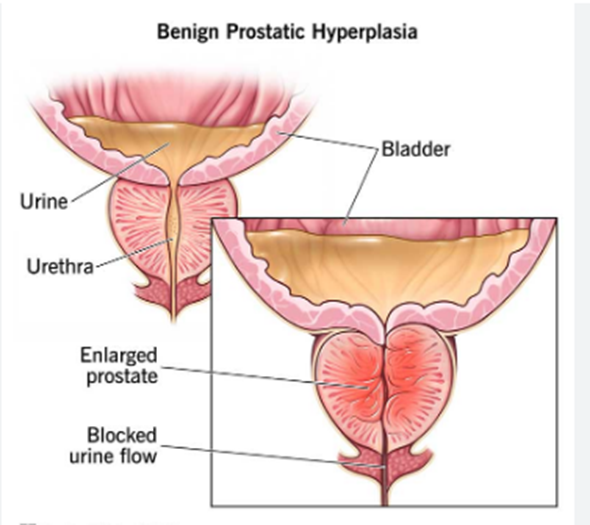
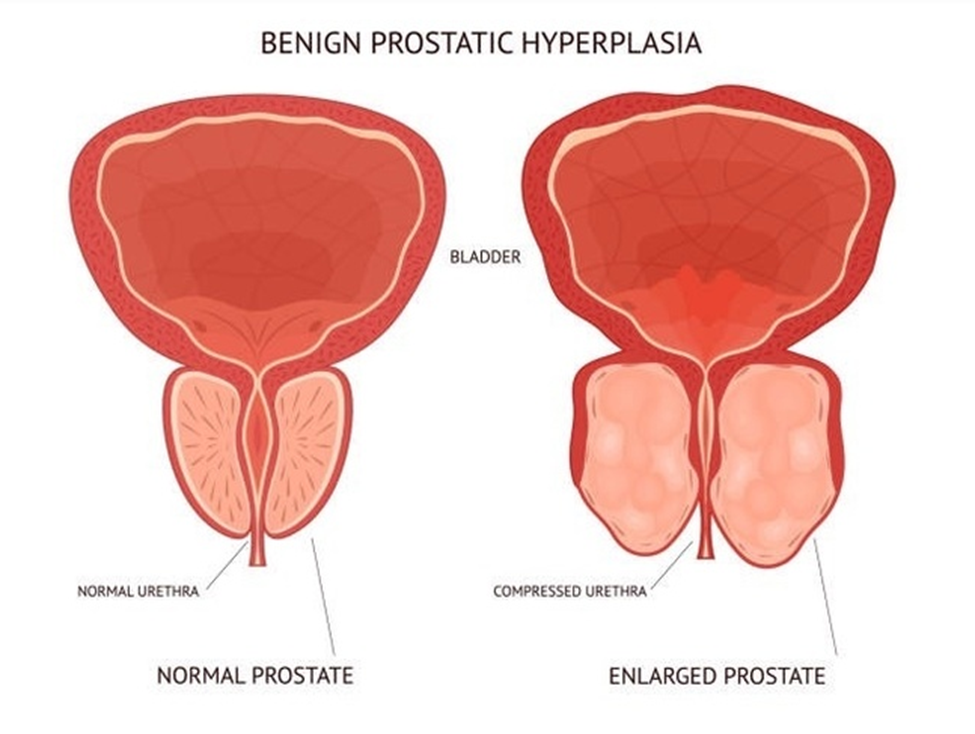
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
An enlarged prostate is known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It's a rise in the prostate gland's size. In older men, BPH is fairly frequent. It has nothing to do with prostate cancer.
The pressure that a bigger prostate can exert on the urethra causes BPH symptoms. The urethra is a thin tube that connects the bladder to the outside world.
Men with BPH may have a strong need to urinate regularly. When they do go, they may have a weak stream of urine and the sensation that their bladder is not emptied after urination. Your doctor may choose to manage this issue by just monitoring it or prescribing drugs like alpha-blockers.
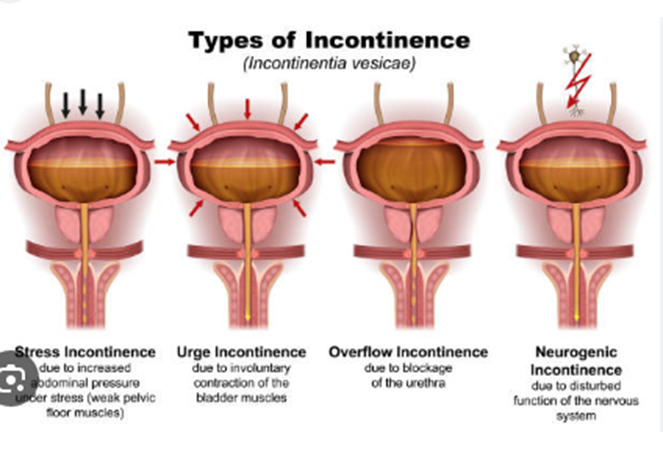
Urinary Incontinence
The loss of bladder control is known as urinary incontinence. Urine leakage occurs as a result of this condition. Although difficult and unsightly, this ailment is far from commonplace. Incontinence affects millions of people. Incontinence can be caused by a variety of factors. The following are a few of the most typical causes: pregnancy or delivery with diabetes, a hyperactive bladder, prostate enlargement, bladder muscles that are weak, Muscles of the sphincter are weak (muscles supporting the urethra), Infections of the urinary tract. Parkinson's disease and multiple sclerosis are examples of such disorders. In some circumstances, simple lifestyle modifications such as limiting fluid intake may be sufficient to solve the condition. If none of these methods work, your doctor may recommend surgery to address the underlying problem.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are caused by harmful bacteria or viruses invading the urinary tract and causing infection. They are far more common in women, though they can sometimes affect men. According to statistics, approximately 40% of females and 12% of males may experience a UTI with apparent symptoms at some point in their life. One of the symptoms of a UTI is a burning sensation when urinating. Urge to urinate frequently and the impression that the bladder is not empty after urinating are two further symptoms. Most UTIs can be cleared completely in five to seven days with antibiotics.

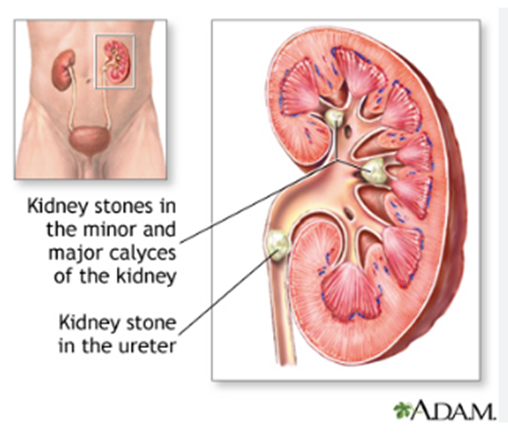
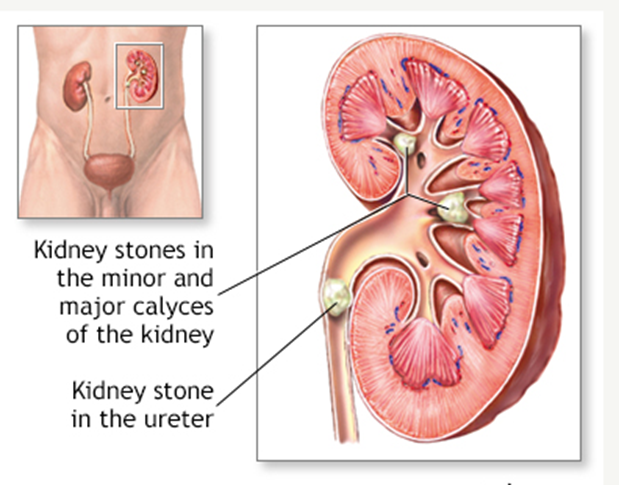
Kidney and Ureteral Stones
When there are crystals in the urine and minute particles surround and settle on these crystals, stones form in the kidneys. Stones that go from the kidney to the ureter are known as ureteral stones (the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder).
These stones can obstruct urine flow and create a lot of discomforts. Many people can evacuate small stones without medical assistance, but larger stones might cause obstruction, which is troublesome.
In some cases, medical or surgical procedures may be required to remove big stones. One of the most often utilised procedures is extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). The process involves breaking stones into smaller bits with sound waves so that they can exit the body more easily.
Other Common Urological Conditions
Prostate cancer, bladder cancer, bladder prolapse, hematuria (blood in the urine), erectile dysfunction (ED), interstitial cystitis (also known as painful bladder syndrome), hyperactive bladder, and prostatitis are some more prevalent urological diseases (swelling of the prostate gland).
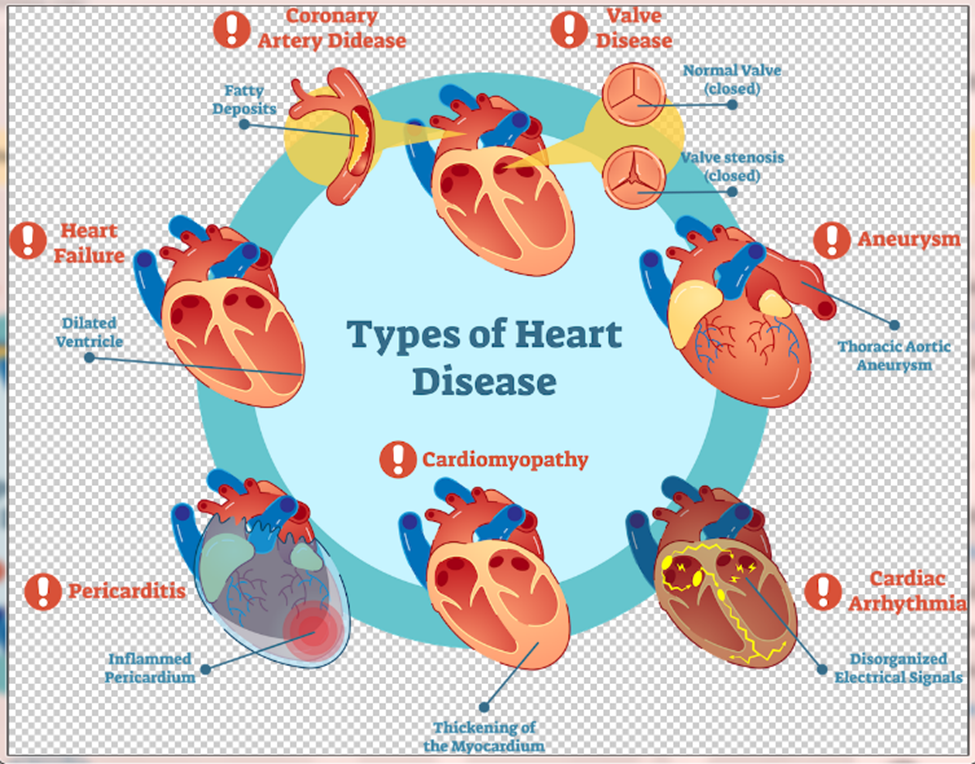
Cardiovascular disease is a group of diseases affecting your heart and blood vessels. These diseases can affect one or many parts of your heart and/or blood vessels. A person may be symptomatic (physically experiencing the disease) or asymptomatic (not feeling anything at all).
Cardiovascular disease includes heart or blood vessel issues, including:
Cardiovascular disease symptoms can vary depending on the cause. Older adults and people assigned female at birth may have more subtle symptoms. However, they can still have serious cardiovascular disease.
Symptoms of Heart Issues :-
Symptoms of Blockages in blood vessels :-
Conditions of Heart Diseases
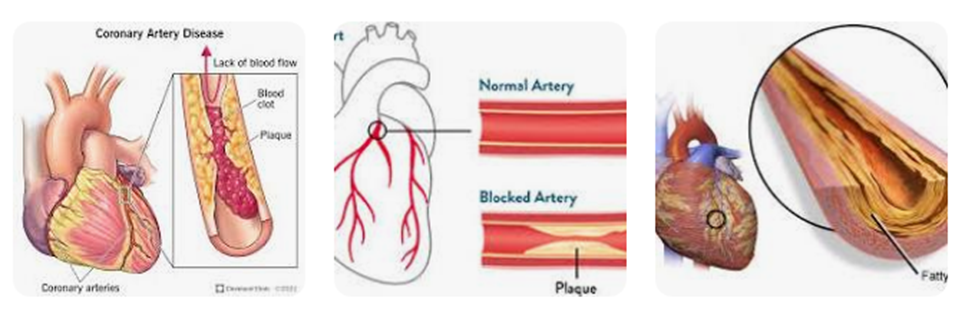
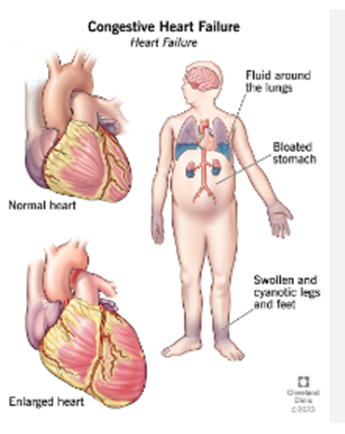
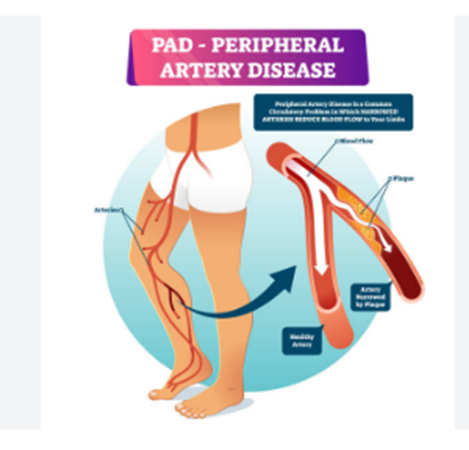
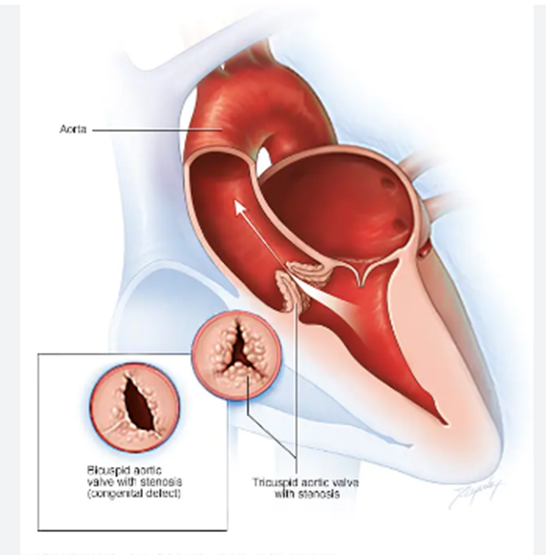
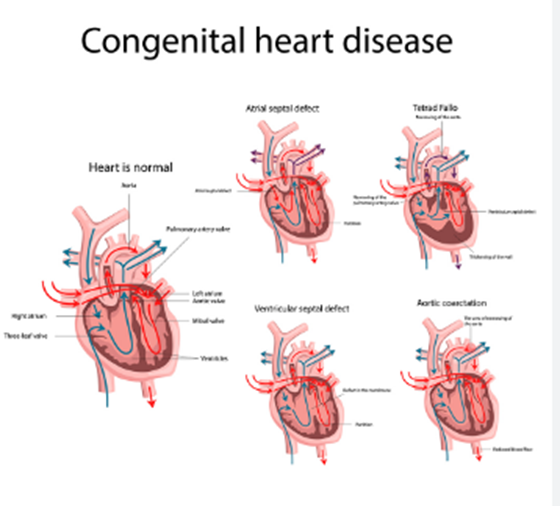
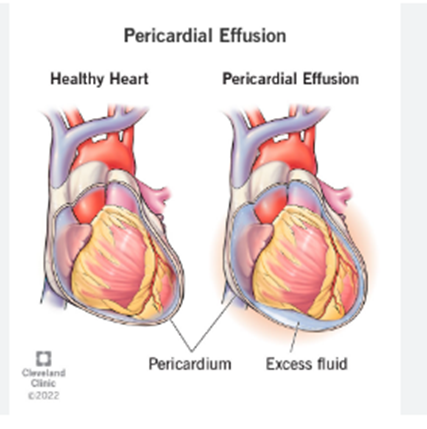
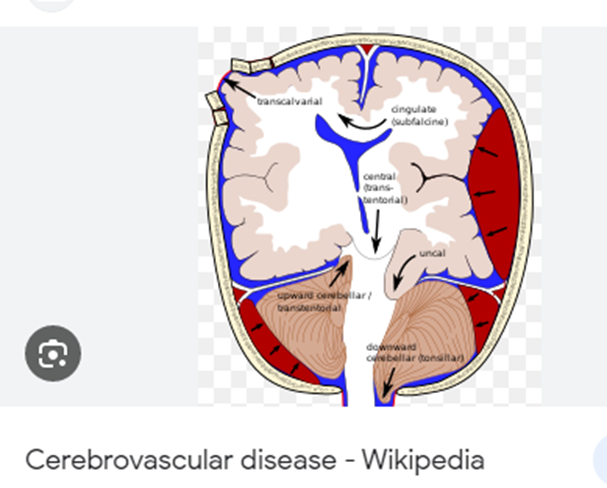
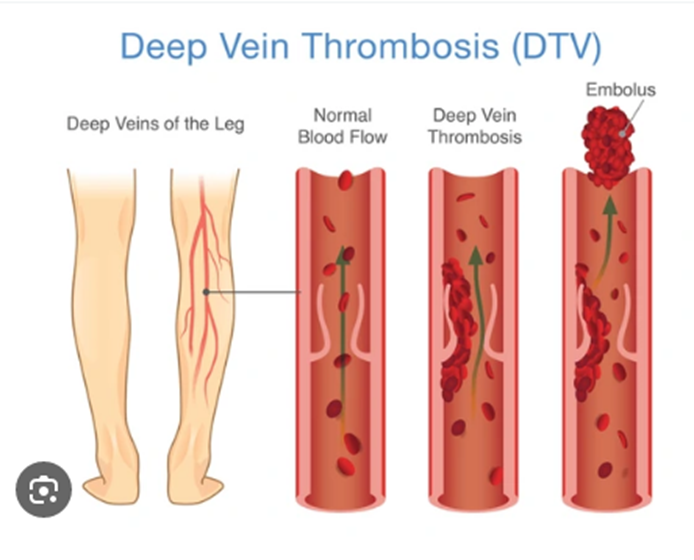
Cold Sores
Also called fever blisters, you don't get cold sores from fevers or colds but they can be triggered by them. The virus that causes cold sores is usually passed via a kiss, shared utensils, or other close contact. Over-the-counter creams and ointments may help discomfort and speed healing. Frequent sores may require a prescription. Cold sores are a top mouth problem. Other problems include canker sores, TMJ, bad breath, and mouth cancer.
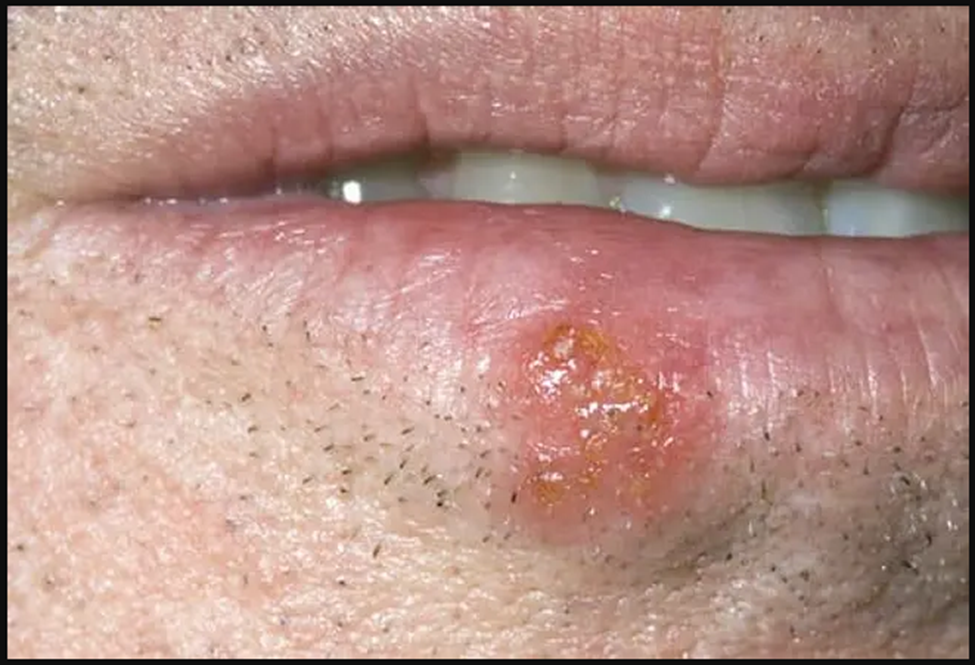
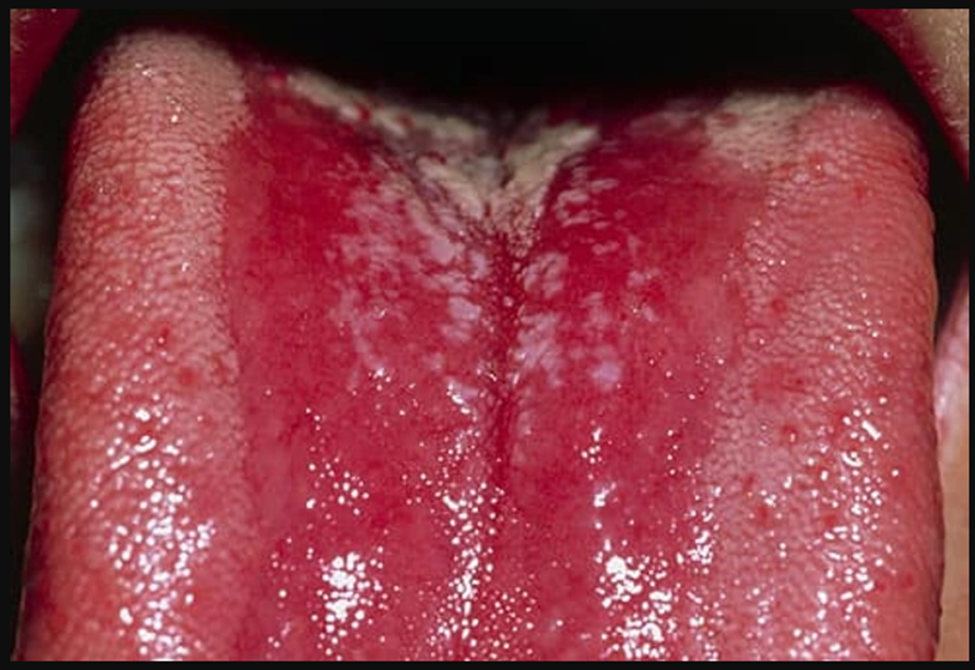
Thrush
Caused by candida yeast, thrush is most common in older adults or babies. But a weakened immune system, antibiotics, diabetes, or certain medications -- such as inhaled corticosteroids -- can give candida a chance to grow wild. Wiping away the patches will cause soreness. See a doctor for a firm diagnosis.
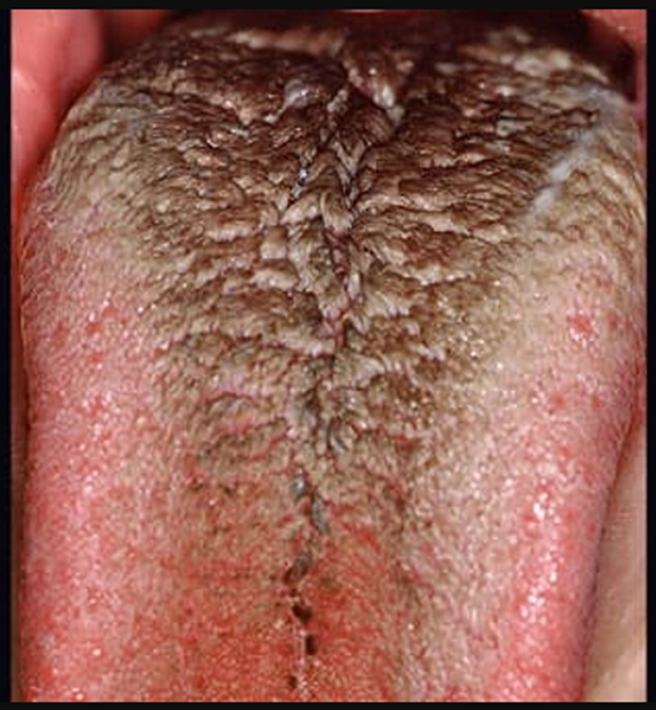
Black Hairy Tongue
This painless condition occurs when the little bumps on your tongue grow long and trap bacteria that live in your mouth -- making the tongue look black and hairy. Causes can include antibiotic use, poor oral hygiene, smoking, drinking a lot of tea or coffee, and not producing enough saliva. Brushing the tongue and using a tongue scraper is usually all you need to treat it, though sometimes medication is necessary.
Canker Sores
No one knows what causes these small, painful blisters inside your mouth. Triggers include hypersensitivity, infection, hormones, stress, and not getting enough of some vitamins. Also called aphthous ulcers, canker sores can show up on the tongue, cheek, even your gums. They usually last a week or two. Persistent, severe canker sores can be treated with numbing creams, prescription drugs, or dental lasers.
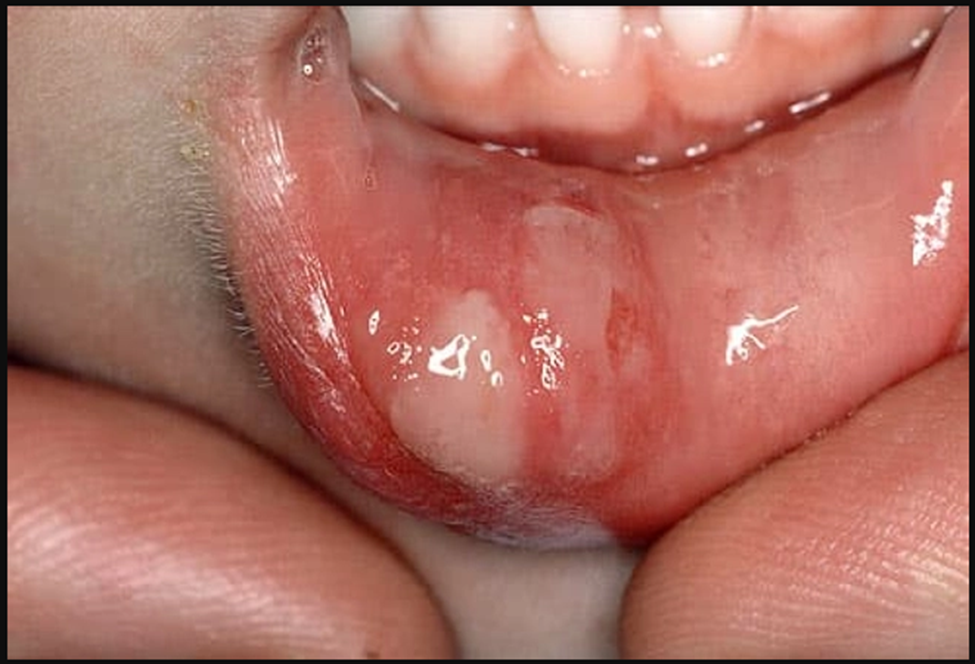
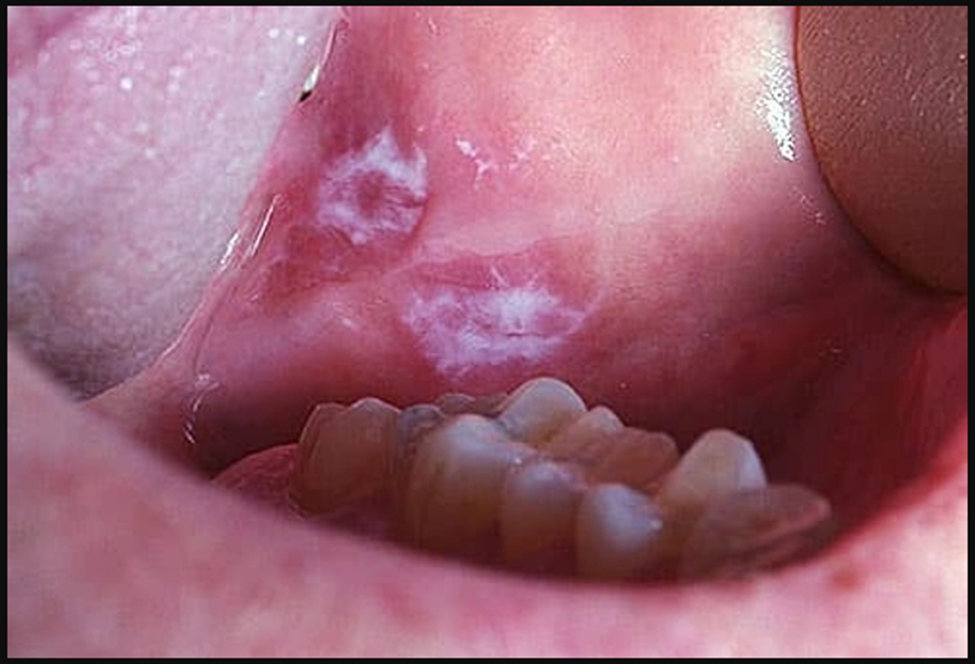
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia is a reaction to an irritant, like rough teeth, badly fitting dentures, smoking, and smokeless tobacco. It can show up as white patches or plaques in the mouth, is usually painless, and can't be scraped off. Leukoplakia can also be a precancerous condition. Persistent patches or other changes in your mouth need a dentist's evaluation.
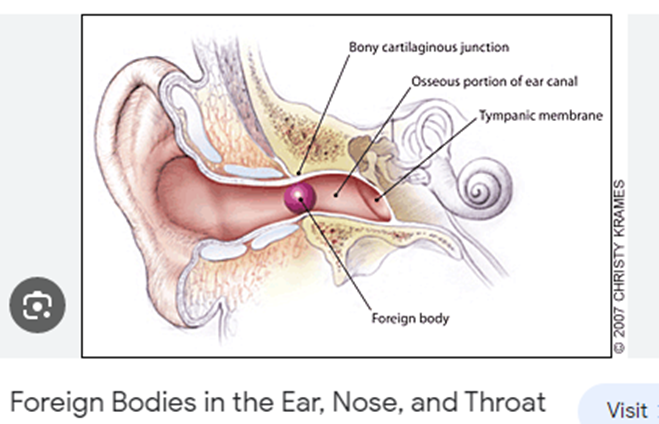
Ear, nose and throat consultants treat a wide range of different conditions that can affect these connected parts of the body. The ENT disorders that we treat most often can be divided into five main types, although we can also help with other kinds of ear, nose and throat problems as well as other issues such as balance disorders.
Infections
Infections are one of the most common problems treated by ear, nose and throat consultants. Many different types of infection can cause ENT disorders. You could have a bacterial infection that we can treat with antibiotics or a viral infection that won't respond to these drugs. The infection could also affect different parts of your ear, nose and throat.

Injuries
Injuries to the ear, nose or throat can be very painful and difficult, especially if they affect your senses or interfere with eating and drinking. If you have an injury in any of these areas then you may need to see ear, nose and throat consultants during your recovery. For example, a severe injury to your nose might need to be treated with rhinoplasty surgery to ensure you can breathe clearly. In most cases, surgery won't be needed, but there might be other procedures we can perform to help you to recover.
Foreign Objects
Ear, nose and throat consultants often have to help patients who have foreign objects stuck in one of these passageways. It is much more common in children, who often stick toys or other objects into their nose or ears. However, even adults can get a piece of food stuck in their throat or lose an item while trying to clean their ear. We don't recommend sticking anything in your ear, nose or throat, unless you are eating it. If you do, it could cause damage or lead to an infection. We might need to use specialist tools to remove the object safely.
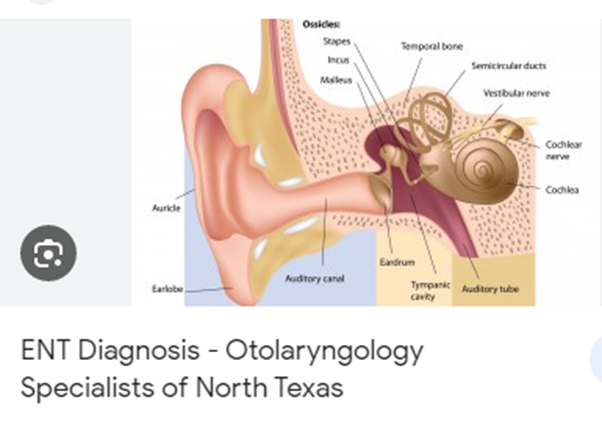
Functional ENT Disorders
The ears, nose and throat all have essential roles to play including for our senses, speech, breathing and eating. ENT disorders can sometimes get in the way of these essential functions, causing symptoms such as:
If you're experiencing these kinds of problems then you may need to see ear, nose and throat consultants to find out why. The treatment we provide can often help to improve your symptoms or at least help you to manage them. For example, getting fitted with hearing aids could have a dramatic impact on your daily life if you've been struggling to follow conversations.
Lumps and Growths
Ear, nose and throat consultants can also help to diagnose any unusual growths that appear in these areas or elsewhere on the head and neck. It's always important to get any abnormal growths, swelling or lesions checked as there is a chance that it could be something serious such as cancer. In most cases, the symptoms will usually be caused by other kinds of ENT disorders. For example, you might have benign throat nodules or enlarged turbinates that are blocking your nose. However, in some cases lumps and growths can be caused by cancer. The sooner that you are diagnosed with cancer, the better the chances that the treatment will be successful. This is why it is so important to see an ENT specialist if you notice any unusual lumps or growths.
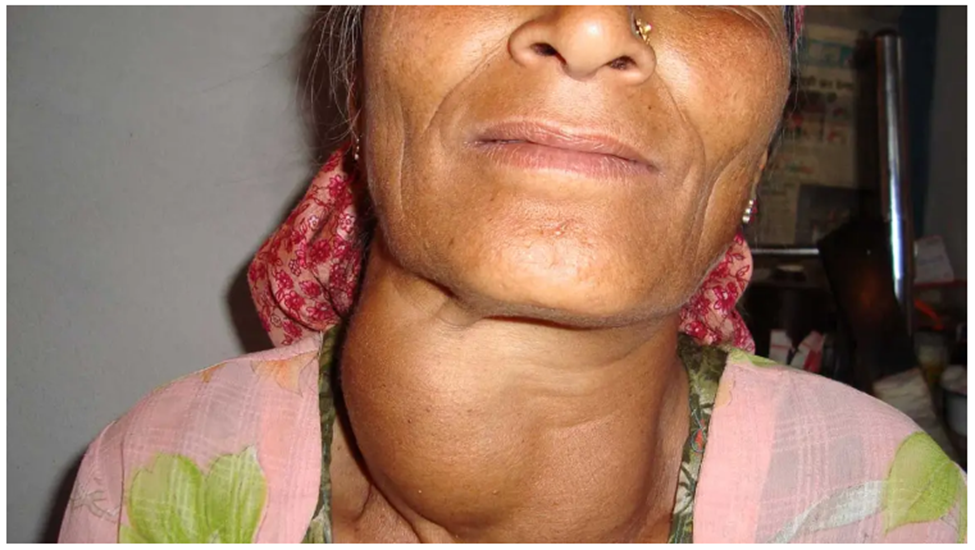
Ear, nose and throat consultants treat a wide range of conditions that affect some of the most hardworking and sensitive parts of our bodies. Some of the most common ENT disorders that we see in the clinic are infections, injuries, foreign objects, functional issues and growths. All of these ENT disorders can affect the ears, nose and the throat in different ways. However, ENT specialists are experts in all kinds of disorders affecting the head and neck, so we also treat patients with many other conditions. If you have any worries about your ear, nose, throat, balance, head or neck then you may need to see an ENT doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
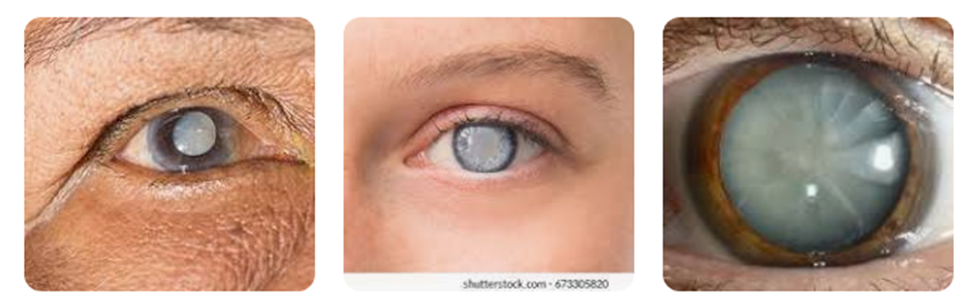
Cataract
A cataract is a clouding of your eye's lens. This cloudy lens can develop in one or both eyes. Cataracts are the world's leading cause of blindness. In the U.S., cataracts is the leading cause of reversible vision loss. Cataracts can occur at any age and even be present at birth, but are more common in people over the age of 50.
Symptoms of a cataract include :-
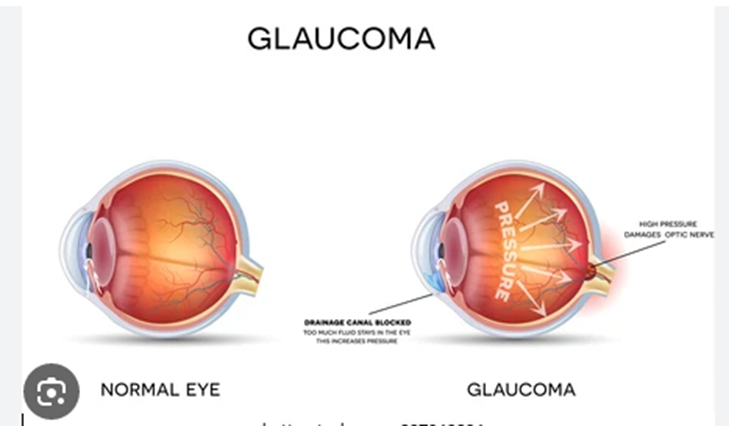
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disease that results from higher-than-normal fluid pressure in the eye. The pressure damages your optic nerve, which affects how visual information is transmitted to your brain. Undetected and untreated glaucoma can lead to vision loss and blindness in one or both eyes. Glaucoma often runs in families.
There are two main types of glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and you may not notice vision change until the disease is far along. Closed-angle glaucoma can happen suddenly. It's painful and causes loss of vision very quickly.
Symptoms include:-
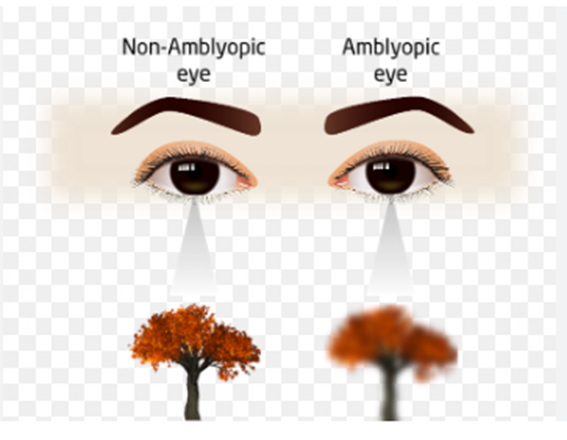
Amblyopia
Amblyopia: Amblyopia (also called "lazy eye") happens when your child's brain and one eye aren't working together properly and the brain favors the other better-seeing eye. They'll have reduced vision in the non-favored eye. This is the most common cause of vision impairment in children.
Strabismus
Strabismus:Strabismus is a lack of coordination between your child's eyes, which causes the eyes to cross or turn out. Your child's eyes don't focus together on a single image at the same time. This can cause reduced 3D vision and/or the brain may favor one eye over the other, which can cause loss of vision in the non-favored eye (amblyopia, see above).
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis: Conjuctivitis, also known as pink eye, is an inflammation of the clear tissue that lines the inside surface of your eyelid and the outer coating of your eye. This tissue is called conjunctiva. It helps keep your eyelid and eyeball moist. Pink eye can be highly contagious, especially among children. Although it doesn't damage vision, it causes itchy, red, blurry, tearing and discharge.
One of the first signs of muscle problems is muscle weakness. This means the muscle lacks strength and cannot do its job. Many different diseases can cause muscles to become weak.
Muscle pain that improves with home therapies is usually nothing to worry about. Pain from severe injuries or a serious illness that affects the whole body often requires medical care.
Seek immediate medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms:
People with muscle disease may also experience muscle spasms, cramping, or twitching.
Other symptoms of muscle diseases include:
A muscle disease is any disease that affects the human muscle system. Primary muscle diseases result from abnormalities of the muscles themselves. Secondary muscle diseases are caused by another condition that may have triggered or caused the muscle disease.
Primary muscular system diseases include:
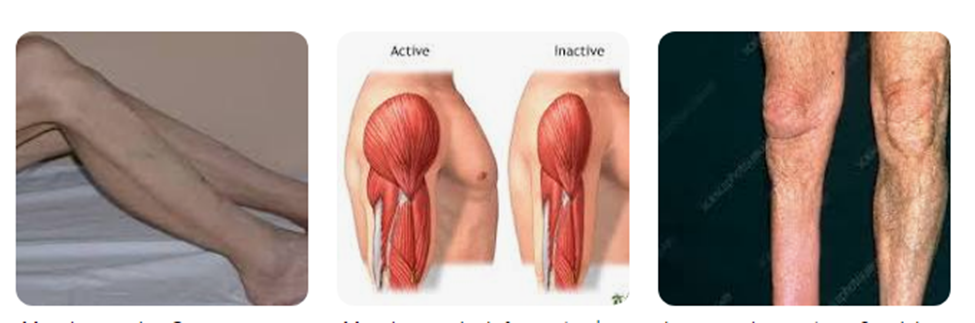

Both primary and secondary muscular system diseases affect the muscles and sometimes the nerves that supply them. Because of this, these diseases may eventually result in muscle wasting, or loss of muscle mass. This may involve loss of strength and function in one or more muscles. Sometimes paralysis may occur.
General symptoms of bone disease may include:
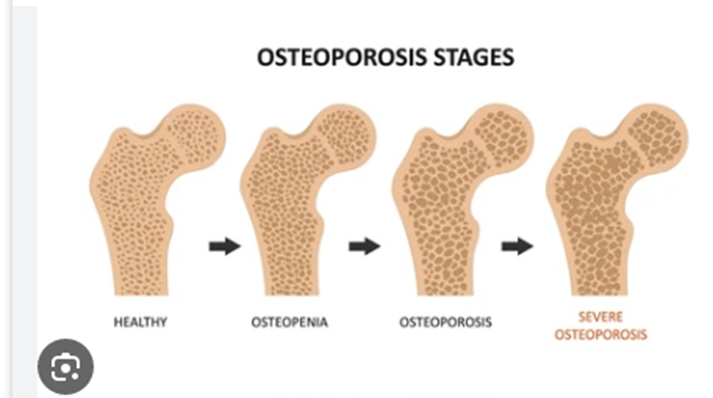
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease that results in a decrease in bone mass and mineral density. The quality and structure of the bone may also change. Osteoporosis can decrease bone strength and increase the risk of fracturing.
The risk of osteoporosis increases with age and affects people of all ethnic groups. It most commonly affects non-Hispanic white females and Asian females.
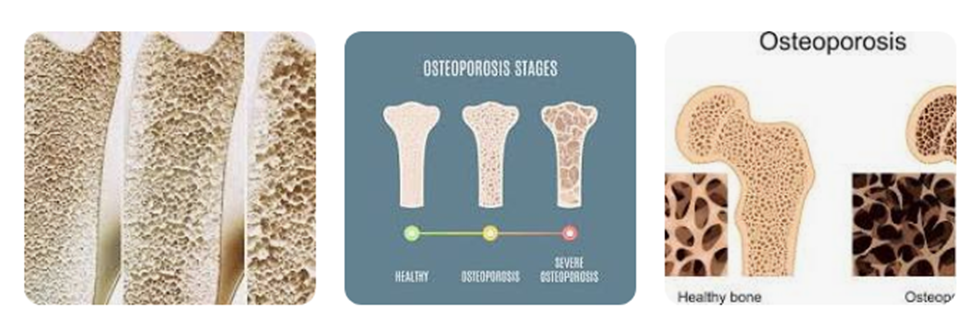
Osteopenia
Osteopenia refers to a decrease in bone mineral density below a normal level but not low enough for a doctor to classify it as osteoporosis. A T-score is a measure of bone density. A person with a T-score between -1 and -2.5 will receive a diagnosis of osteopenia, whereas a doctor would classify a T-score lower than -2.5 as osteoporosis. The prevalence of osteopenia is 4 times higher in females compared with males.
Paget's disease
Paget's disease is a condition that affects the bone remodeling process. This refers to the action by which the body breaks down old bone tissue and replaces it with new bone tissue. In people with this chronic condition, the process of rebuilding bones takes place at a faster rate, resulting in an unusual bone structure. This can either cause the bones to become softer or larger, making them more susceptible to complications such as bending or fractures.
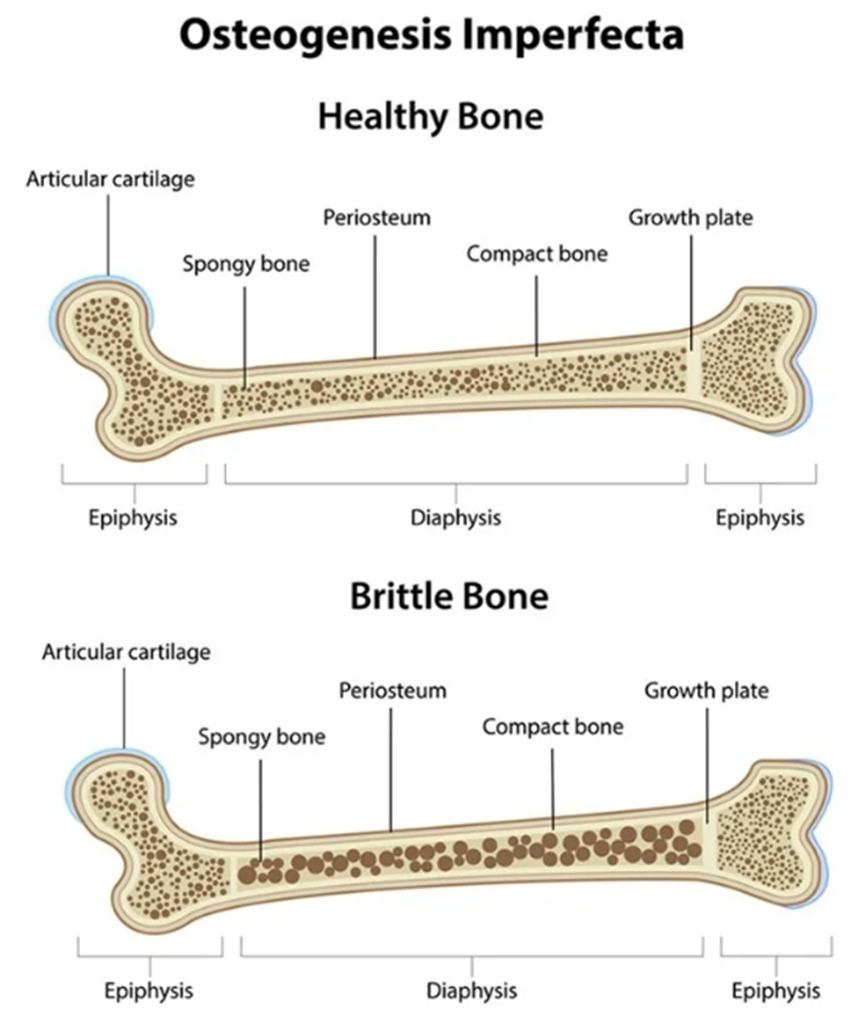
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a disorder that causes the bones to fracture easily. Some people may also refer to OI as brittle bone disease. The condition results from a change or mutation in the genes that carry information for making a protein known as type I collagen. This protein is necessary for strong bones. People with a family history of OI have a higher risk of having the disease as a person can inherit the gene mutation through one or both of their parents. There are different types of OI. The most common and mildest type is type I, while type II is the most severe.
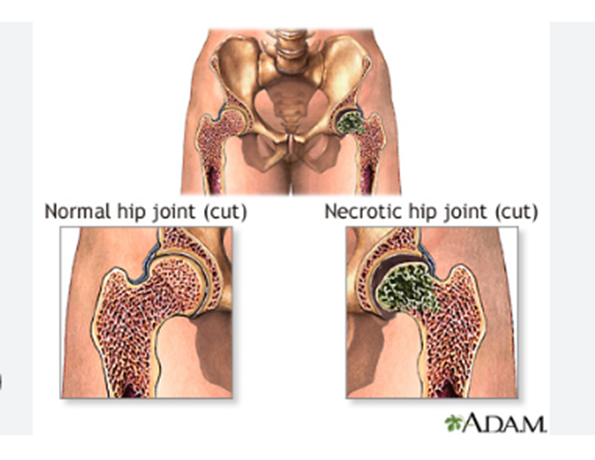
Osteonecrosis
Osteonecrosis, also known as avascular necrosis or aseptic necrosis, occurs when there is a disruption to a bone's blood flow, leading to bone tissue death. This can cause the bone to break down and the joint to collapse. While osteonecrosis may occur in any bone in the body, it commonly affects the shoulders, hips, and knees. The condition occurs most often in people aged 20-50 years. These individuals also often have a history of trauma, corticosteroid use, or excessive alcohol intake.
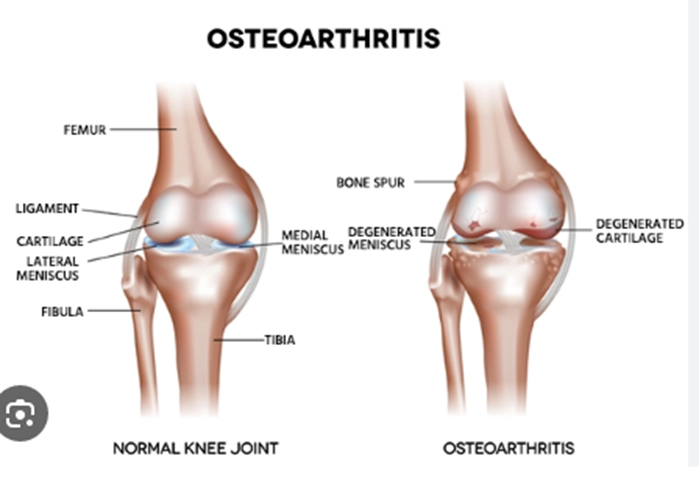
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. This condition affects the body's joints by degrading cartilage, the tissue that covers the surface of joints. Osteoarthritis can also change the shape of bones. Osteoarthritis most frequently affects the hands, hips, and knees.
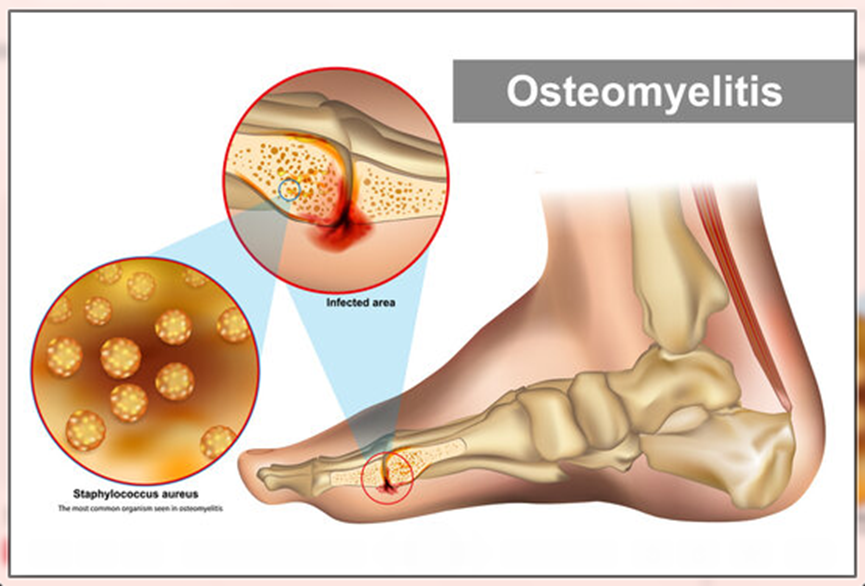
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis describes an infection or inflammation of the bone, with myelitis referring to inflammation of the fatty tissues within the bone. It typically occurs when a bacterial or fungal infection enters a bone from the bloodstream or surrounding tissue. It can happen at any age but is more common in young children.
Fibrous dysplasia
Fibrous dysplasia occurs when abnormal fibrous tissue replaces healthy bone tissue. The unusual scar-like tissue makes the bone weaker. This can cause the bone to change shape and increase the risk of fractures. Fibrous dysplasia typically occurs due to a gene mutation that results in bone cells producing an abnormal type of fibrous bone. While it can develop in any bone, it occurs most often in the thigh bone, shin bone, ribs, skull, humerus, and pelvis.
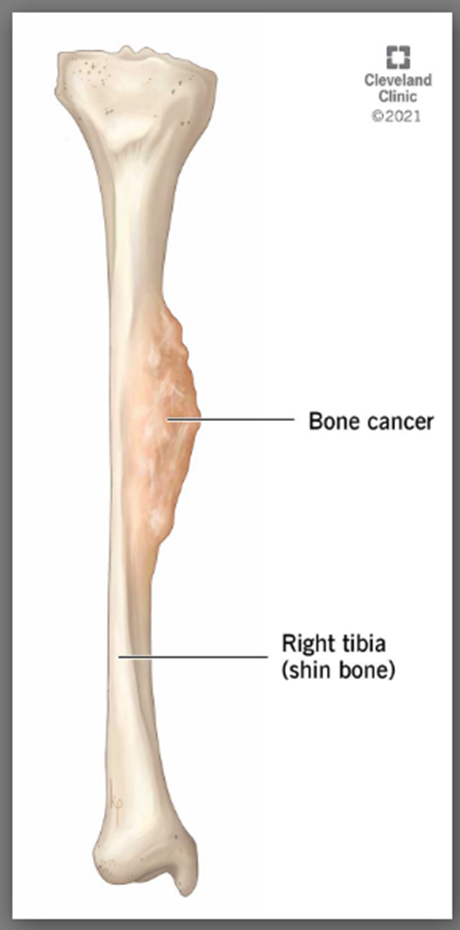
Bone cancer and tumors
Bone cancer is an uncommon type of cancer that begins when cells in a bone start to grow out of control. Any of the cells in the bone can develop into cancer. Primary bone cancers are cancers that start in the bone. The most common types of primary bone cancers include osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma. Cancer cells can also spread to the bone from other areas of the body. Doctors refer to these as bone metastases. The most common site for bone metastases is the spine.
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia, also known as bone softening, refers to a condition where the bone does not harden the way it should after forming. This metabolic bone disease occurs when there is incomplete mineralization of the bone. Mineralization refers to the process where minerals coat the inner layer of the bone, forming a hard outer shell. The incomplete formation of this shell leaves the collagen soft and vulnerable.
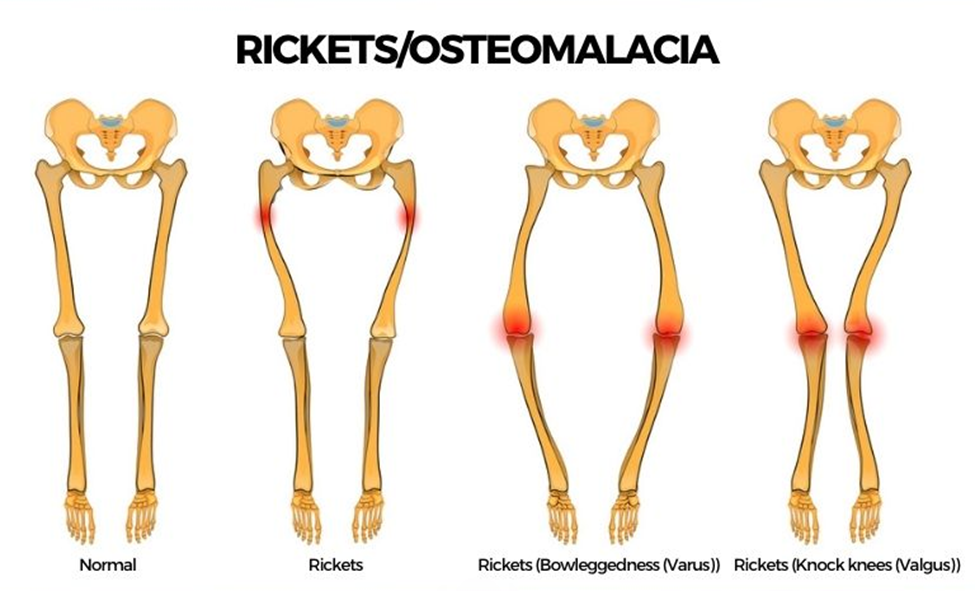
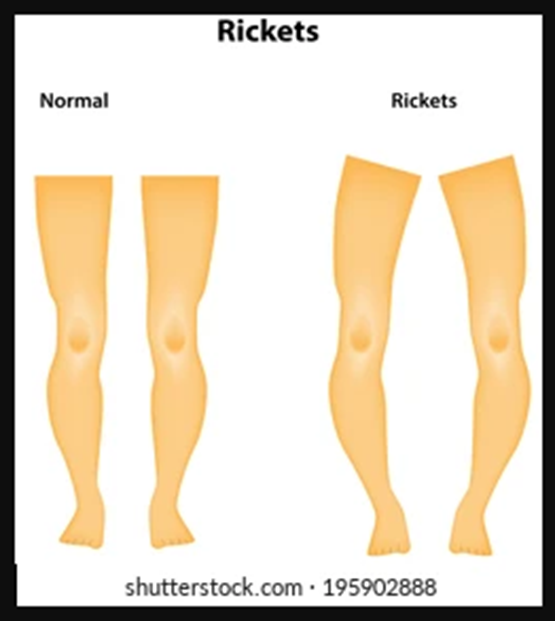
Rickets
Rickets is a childhood bone condition similar to osteomalacia, but it occurs due to imperfect mineralization. It results in soft, weak bones, typically due to a vitamin D deficiency. Without sufficient vitamin D, the body cannot metabolize calcium and phosphorous, which are essential for proper bone development and growth. Vitamin D deficiency may result from inadequate nutrition, lack of sun exposure, or malabsorption.
Autoimmune conditions
An autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system attacks the body's own cells, tissue, and organs. Bone diseases can develop secondary to some autoimmune diseases, increasing the risk of complications such as bone loss and fractures. These conditions include:
Female Sexual Dysfunction
Painful sex. Lack of interest in sex. Unsatisfying sex. These are just some types of a condition called sexual dysfunction. It can be both a cause of infertility and a result of it. If it's hard to conceive and you aren't thrilled with your sex life, there's a chance these things are related. Talk to a health care professional about your problems. It could make getting pregnant more likely and more fun.
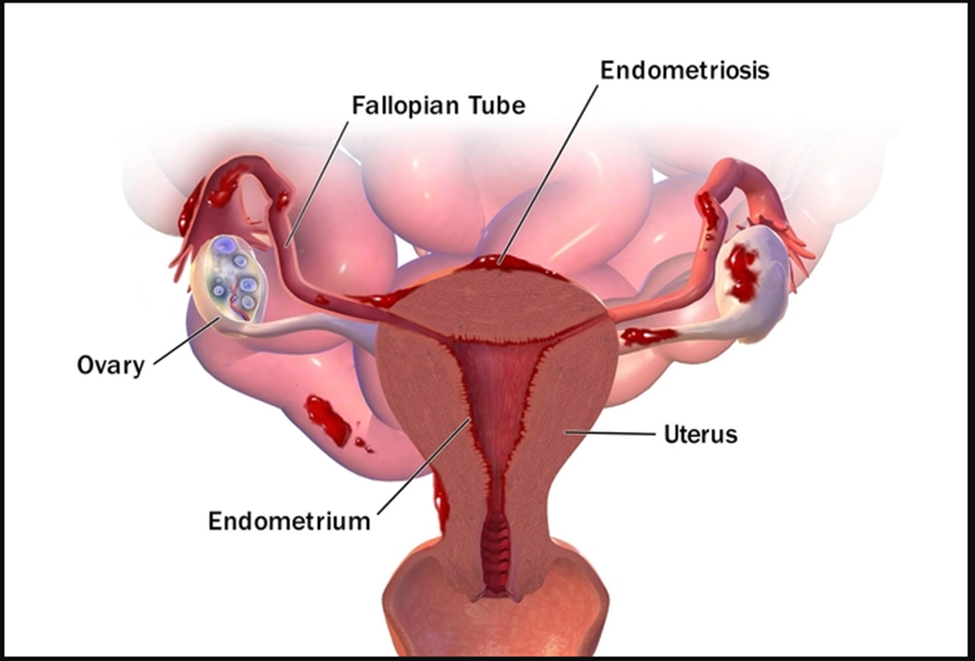
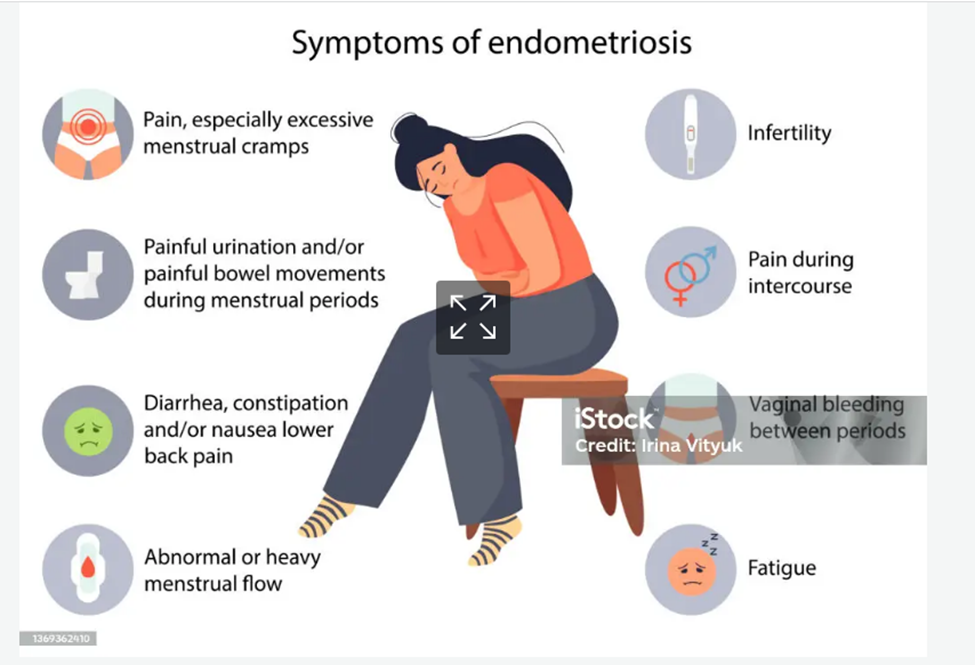
Endometriosis
This happens when the same kind of tissue as the kind that lines the inside of your uterus starts growing in areas other than the uterine lining. The condition is often painful and can affect fertility. In fact, women who have trouble with conception are 6 to 8 times more likely to have endometriosis than fertile women. Surgery or in vitro fertilization can improve the odds of getting (and staying) pregnant.
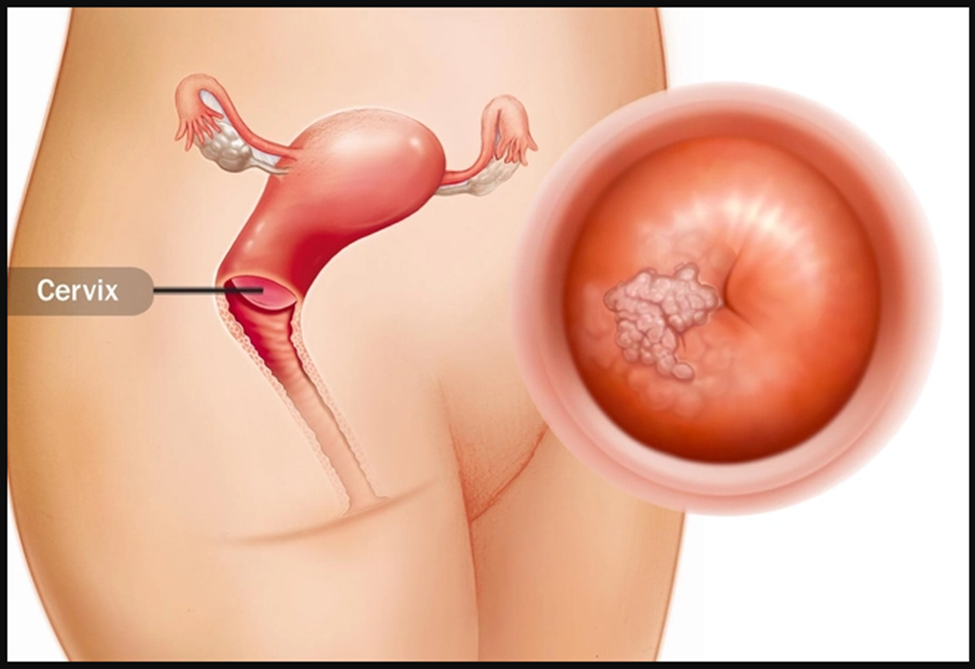
Cervical Cancer
Cancer isn't usually top of mind for young women, but this type -- caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) -- is a serious threat. Each year, more than 11,000 women get the disease. Many are of childbearing age. The upside: Thanks to Pap smears, doctors can find and treat it early. The downside: Many treatments cause infertility. If you get cervical cancer, ask for options that will let you get pregnant later.
HIV
With today's powerful medications, this disease can often be managed like a chronic condition. Some people live so well with the virus that they want to have a baby. However, HIV affects fertility in both men and women. Still, you can become a parent. And with certain infertility treatments and a carefully managed pregnancy, the odds of giving your baby the virus are low.
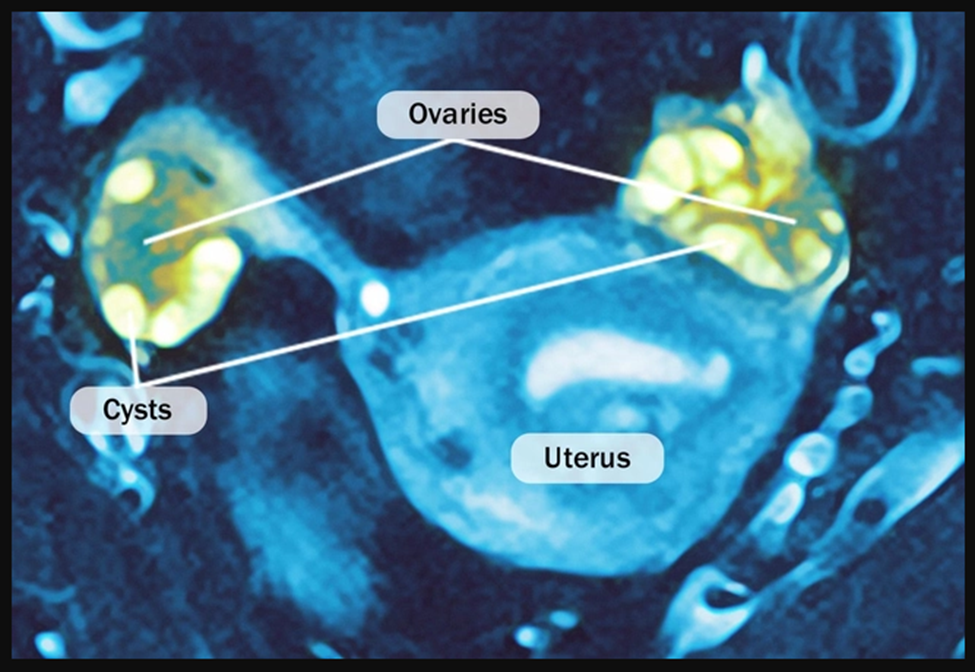
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Many women don't know they have this common cause of infertility until they try to conceive. It's related to a hormone imbalance that affects ovulation and can lead to:
If you have PCOS, ask your doctor what you can do to get pregnant and have a healthy pregnancy.
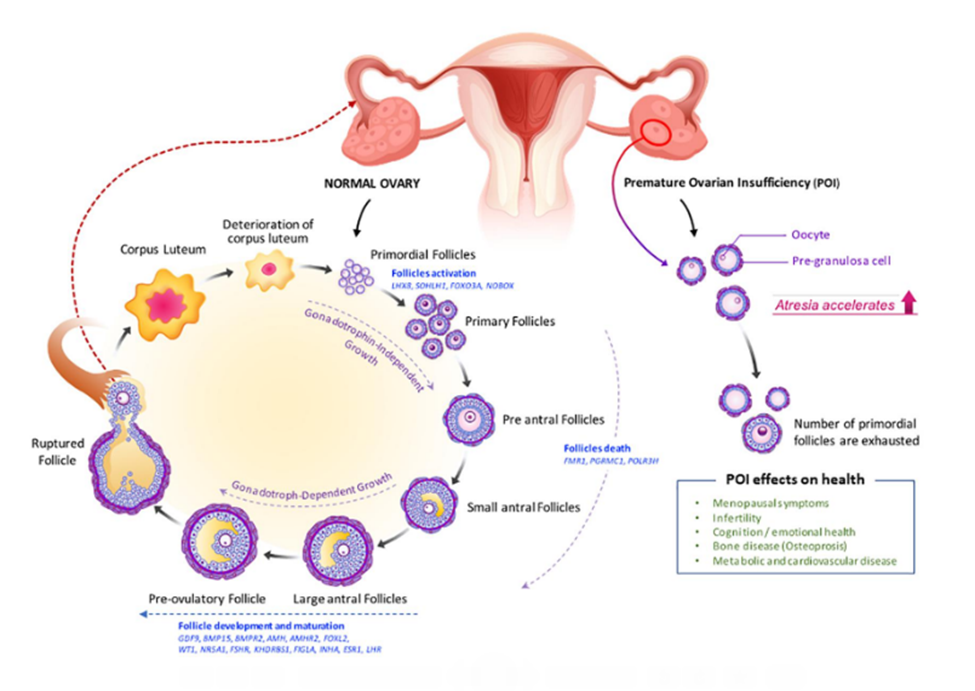
Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI)
If you're under 40, it can cause your ovaries to not work like they should. That means you'll stop getting periods -- or at least stop getting them regularly. Besides monthly problems, women with POI may also have:
Uterine Fibroids
During a pelvic exam, your doctor may find these noncancerous growths on your uterus. They're common, often cause no symptoms, and don't usually stop you from getting pregnant. But they may boost the odds of infertility, miscarriage, or other pregnancy problems for some women. If you want to be a mom, ask your doctor if you should get them treated.
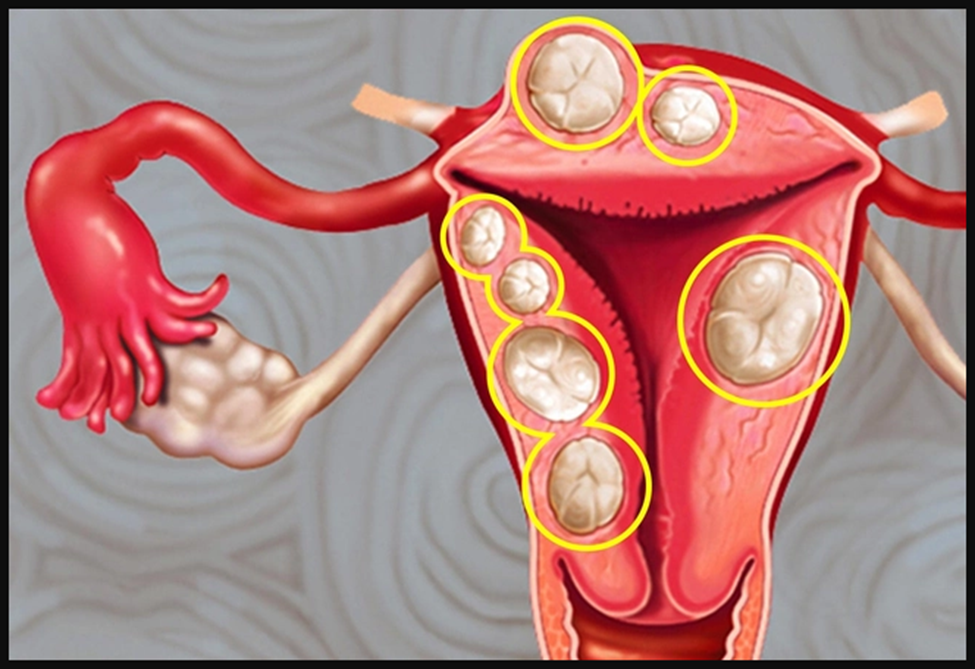
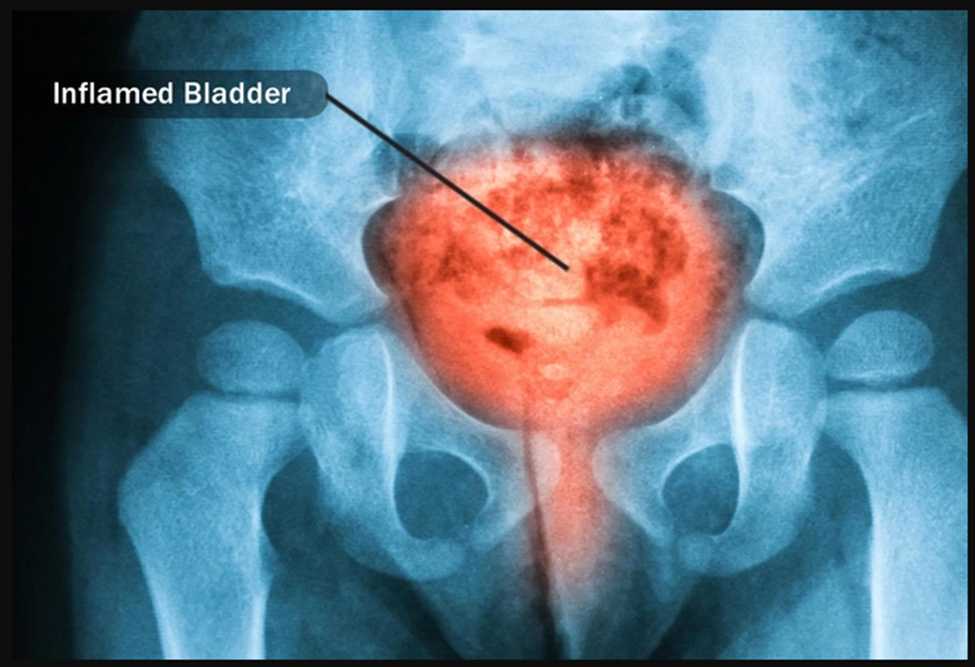
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)
Got IC? Then you know all about the pain and pressure (not to mention the frequent urge to pee) this bladder condition causes. IC won't affect your ability to have a baby, but it sure can torch your sex drive. If you want to conceive but aren't too excited about sex, buy an ovulation kit. It lets you know when you're most fertile, so you can reserve sex for those days.
Excess Body Weight
Those extra pounds can raise your odds of infertility, miscarriage, and other reproductive problems. You don't have to shed half your body weight to make a difference. In a study of overweight women getting fertility treatments, those who lost just 10% of body weight -- that's 17 pounds if you weigh 170 -- were more likely to get pregnant and give birth to a live infant than those who didn't.

Not Enough Body Weight
Unless you're naturally super-thin, being underweight can also cause problems with conception. The problem: You need normal amounts of body fat for pregnancy. Research shows that it's harder to conceive if you weigh too little. It can also raise your chances of miscarriage.

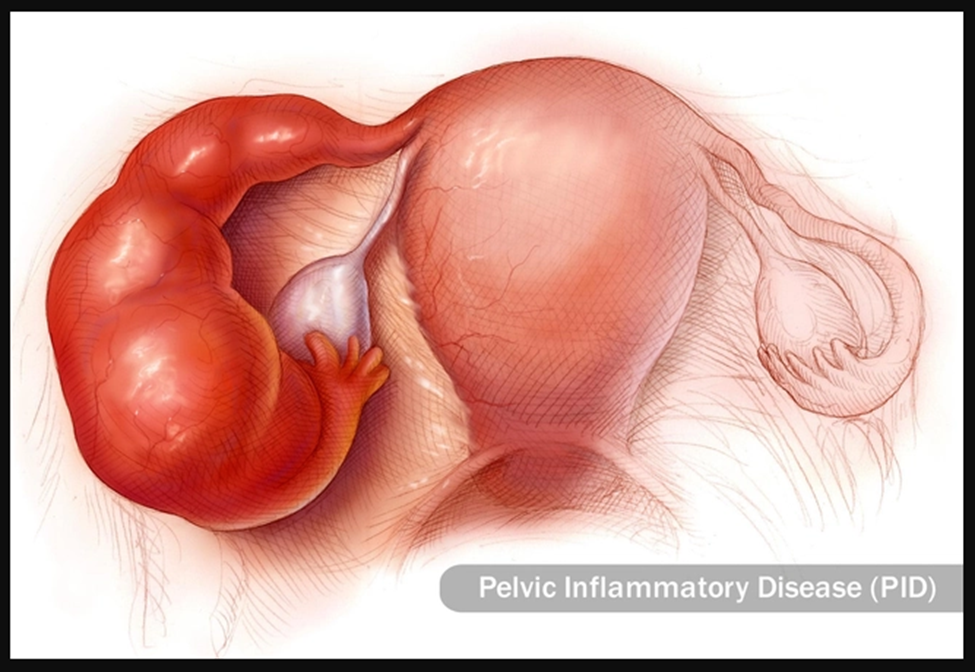
Gonorrhea and Chlamydia
These sexually transmitted infections should be treated promptly. Be sure to see your doctor if you sense something isn't quite right below the belt. Untreated, gonorrhea and chlamydia can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), an infection in your reproductive organs. It can lead to problems like:
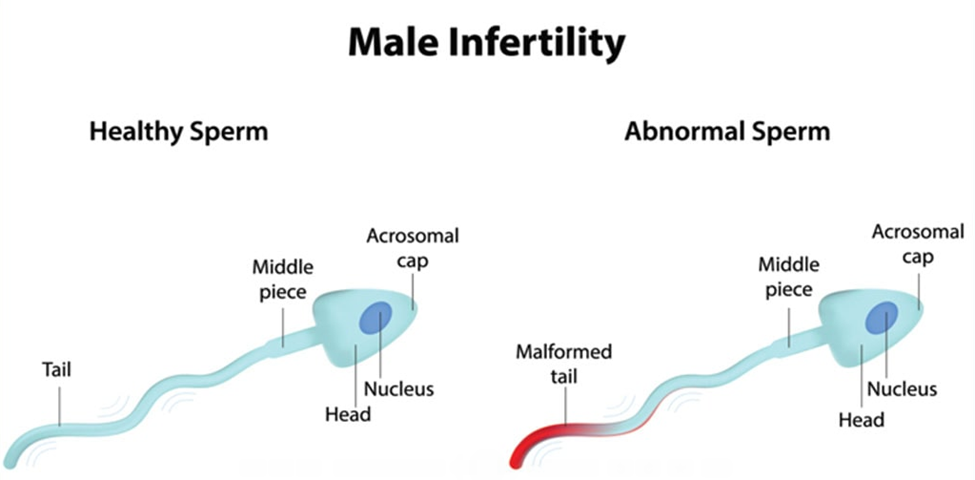
Nearly 1 in 7 couples is infertile, which means they haven't been able to conceive a child even though they've had frequent, unprotected sexual intercourse for a year or longer. In up to half of these couples, Male Infertility plays at least a partial role.
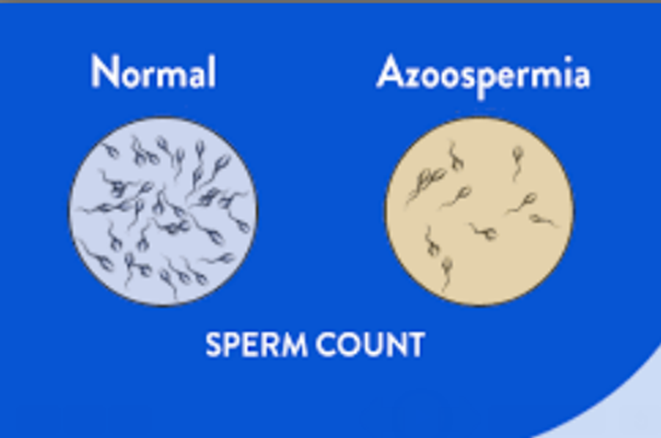
Male infertility can be caused by low sperm production, abnormal sperm function or blockages that prevent the delivery of sperm. Illnesses, injuries, chronic health problems, lifestyle choices and other factors may contribute to male infertility.
The inability to conceive a child can be stressful and frustrating, but a number of treatments are available for male infertility.
Symptoms
The main sign of male infertility is the inability to conceive a child. There may be no other obvious signs or symptoms.
In some cases, however, an underlying problem such as an inherited disorder, hormonal imbalance, dilated veins around the testicle or a condition that blocks the passage of sperm causes signs and symptoms. Signs and symptoms you may notice include:
Infertility is defined as trying to get pregnant with frequent, unprotected sex for at least a year with no success. Infertility results from female factors about one-third of the time and both female and male factors about one-third of the time. The cause is either unknown or a combination of male and female factors in the remaining cases. Female infertility causes can be difficult to diagnose. There are many treatments, depending on the infertility cause. Many infertile couples will go on to conceive a child without treatment.
Symptoms
The main symptom of infertility is the inability to get pregnant. A menstrual cycle that's too long (35 days or more), too short (less than 21 days), irregular or absent can mean that you're not ovulating. There might be no other signs or symptoms.
Your doctor might also want to begin testing or treatment right away if you or your partner has known fertility problems, or if you have a history of irregular or painful periods, pelvic inflammatory disease, repeated miscarriages, cancer treatment, or endometriosis.
Causes
For pregnancy to occur, every step of the human reproduction process has to happen correctly. The steps in this process are:
Female reproductive system
The ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix and vagina, also called the vaginal canal, make up the female reproductive system.
Fertilization and Implantation
During fertilization, the sperm and egg unite in one of the fallopian tubes to form a zygote. Then the zygote travels down the fallopian tube, where it becomes a morula. Once it reaches the uterus, the morula becomes a blastocyst. The blastocyst then burrows into the uterine lining a process called implantation. In women, a number of factors can disrupt this process at any step. Female infertility is caused by one or more of the factors below.
Ovulation Disorders
Ovulating infrequently or not at all accounts for most cases of infertility. Problems with the regulation of reproductive hormones by the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland or problems in the ovary can cause ovulation disorders.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) causes a hormone imbalance, which affects ovulation. PCOS is associated with insulin resistance and obesity, abnormal hair growth on the face or body, and acne. It's the most common cause of female infertility.
Hypothalamic dysfunction
Two hormones produced by the pituitary gland are responsible for stimulating ovulation each month - follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Excess physical or emotional stress, a very high or very low body weight, or a recent substantial weight gain or loss can disrupt production of these hormones and affect ovulation. Irregular or absent periods are the most common signs.
Primary ovarian insufficiency
Also called premature ovarian failure, this is usually caused by an autoimmune response or by premature loss of eggs from your ovary, possibly as a result of genetics or chemotherapy. The ovary no longer produces eggs, and it lowers estrogen production in women under age 40.
Too much prolactin
The pituitary gland can cause excess production of prolactin (hyperprolactinemia), which reduces estrogen production and can cause infertility. This can also be caused by medications you're taking for another condition.
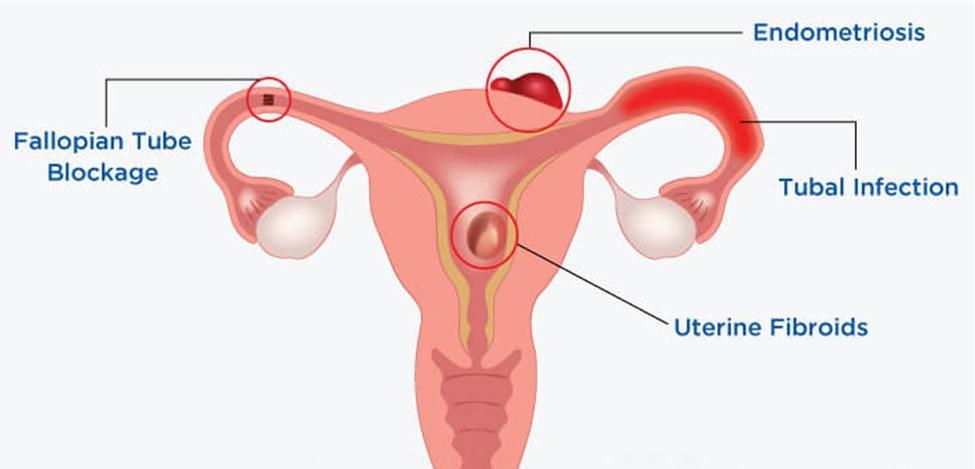
Damage to fallopian tubes (tubal infertility)
Damaged or blocked fallopian tubes keep sperm from getting to the egg or block the passage of the fertilized egg into the uterus. Causes of fallopian tube damage or blockage can include:
Pelvic inflammatory disease, an infection of the uterus and fallopian tubes due to chlamydia, gonorrhea or other sexually transmitted infections
Previous surgery in the abdomen or pelvis, including surgery for ectopic pregnancy, in which a fertilized egg implants and develops somewhere other than the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when tissue that typically grows in the uterus implants and grows in other places. This extra tissue growth - and the surgical removal of it - can cause scarring, which can block fallopian tubes and keep an egg and sperm from uniting.
Endometriosis can also disrupt implantation of the fertilized egg. The condition also seems to affect fertility in less-direct ways, such as damage to the sperm or egg.
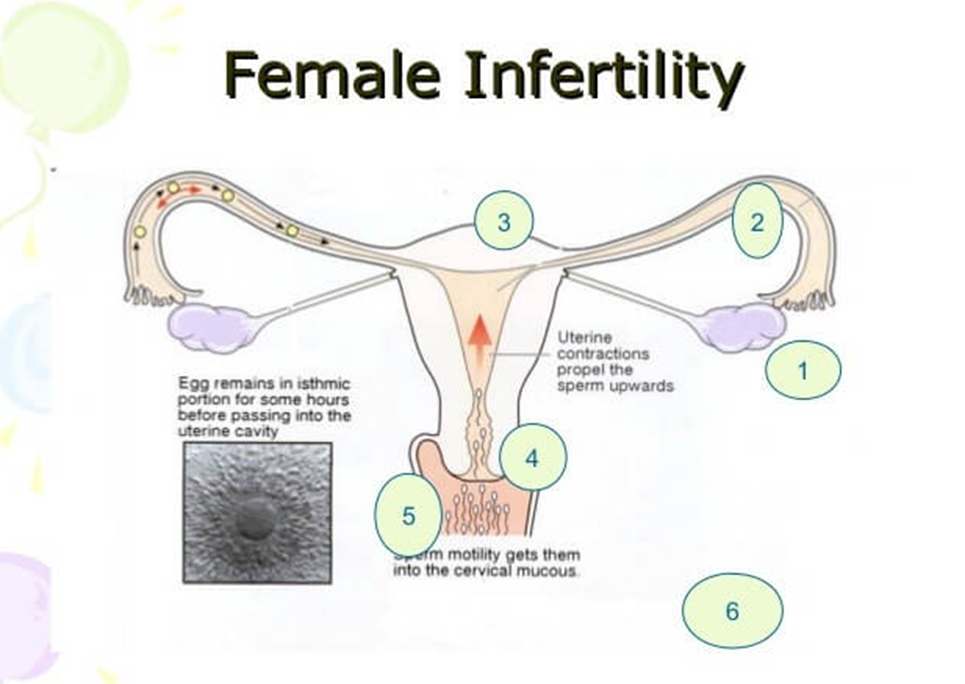
Uterine or cervical causes
Several uterine or cervical causes can interfere with the egg implanting or increase the risk of miscarriage:
Benign polyps or tumors (fibroids or myomas) are common in the uterus. Some can block fallopian tubes or interfere with implantation, affecting fertility. However, many women who have fibroids or polyps do become pregnant.
Problems with the uterus present from birth, such as an unusually shaped uterus, can cause problems becoming or remaining pregnant.
Cervical stenosis, a narrowing of the cervix, can be caused by an inherited malformation or damage to the cervix.
Sometimes the cervix can't produce the best type of mucus to allow the sperm to travel through the cervix into the uterus.
Unexplained infertility
In some cases, the cause of infertility is never found. A combination of several minor factors in both partners could cause unexplained fertility problems. Although it's frustrating to get no specific answer, this problem can correct itself with time. But you shouldn't delay treatment for infertility.
1. Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic (long-lasting) health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy.
Your body breaks down most of the food you eat into sugar (glucose) and releases it into your bloodstream. When your blood sugar goes up, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. Insulin acts like a key to let the blood sugar into your body's cells for use as energy.
With diabetes, your body doesn't make enough insulin or can't use it as well as it should. When there isn't enough insulin or cells stop responding to insulin, too much blood sugar stays in your bloodstream. Over time, that can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease.

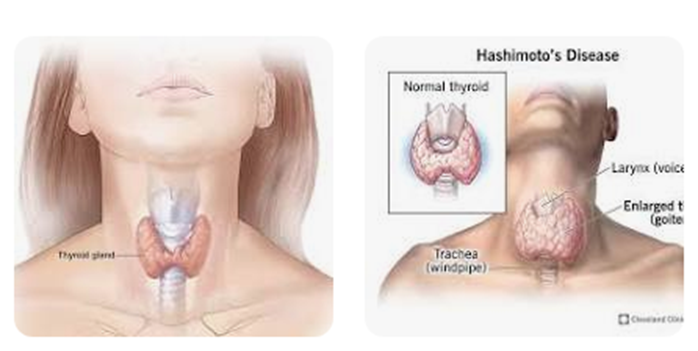
2. Thyroid Diseases
Your thyroid creates and produces hormones that play a role in many different systems throughout your body. When your thyroid makes either too much or too little of these important hormones, it's called a thyroid disease. There are several different types of thyroid disease, including hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis and Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Thyroiditis: This condition is an inflammation (swelling) of the thyroid gland. Thyroiditis can lower the amount of hormones your thyroid produces.
Hashimoto's thyroiditis: A painless disease, Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition where the body's cells attack and damage the thyroid. This is an inherited condition.
Postpartum thyroiditis: This condition occurs in 5% to 9% of women after childbirth. It's usually a temporary condition.
Iodine deficiency: Iodine is used by the thyroid to produce hormones. An iodine deficiency is an issue that affects several million people around the world.
A non-functioning thyroid gland: Sometimes, the thyroid gland doesn't work correctly from birth. This affects about 1 in 4,000 newborns. If left untreated, the child could have both physical and mental issues in the future. All newborns are given a screening blood test in the hospital to check their thyroid function.
Graves' disease: In this condition the entire thyroid gland might be overactive and produce too much hormone. This problem is also called diffuse toxic goiter (enlarged thyroid gland).
Nodules: Hyperthyroidism can be caused by nodules that are overactive within the thyroid. A single nodule is called toxic autonomously functioning thyroid nodule, while a gland with several nodules is called a toxic multi-nodular goiter.
Thyroiditis: This disorder can be either painful or not felt at all. In thyroiditis, the thyroid releases hormones that were stored there. This can last for a few weeks or months.
Excessive iodine: When you have too much iodine (the mineral that is used to make thyroid hormones) in your body, the thyroid makes more thyroid hormones than it needs. Excessive iodine can be found in some medications (amiodarone, a heart medication) and cough syrups.
3. Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a common condition that affects the body's arteries. It's also called hypertension. If you have high blood pressure, the force of the blood pushing against the artery walls is consistently too high. The heart has to work harder to pump blood.
Few people with high blood pressure may have:

Low blood pressure is generally considered a blood pressure reading lower than 90 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) for the top number (systolic) or 60mm Hg for the bottom number (diastolic).
Low blood pressure (hypotension) symptoms may include:
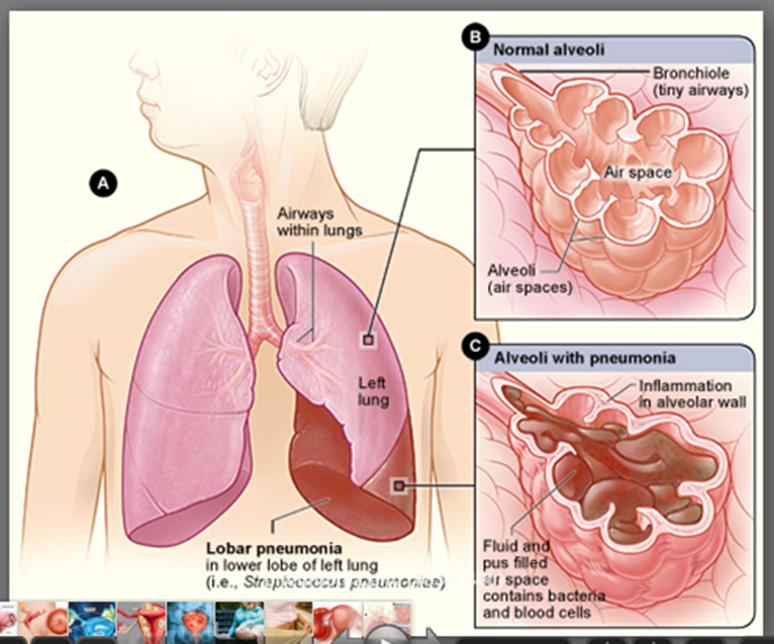
4. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that affects one or both lungs. It causes the air sacs, or alveoli, of the lungs to fill up with fluid or pus. Bacteria, viruses, or fungi may cause pneumonia. Symptoms can range from mild to serious and may include a cough with or without mucus (a slimy substance), fever, chills, and trouble breathing. How serious your pneumonia is depends on your age, your overall health, and what caused your infection.
5. Bronchitis
Bronchitis is when the airways leading to your lungs (trachea and bronchi) get inflamed and fill with mucus. You get a nagging cough as your body tries to get rid of the mucus. Your cough can last two or more weeks. Acute bronchitis is usually caused by a virus and goes away on its own. Chronic bronchitis never really goes away but can be managed.
SYMPTOMS :
Shortness of Breathing
Fever
Runny nose
Tiredness (fatigue)
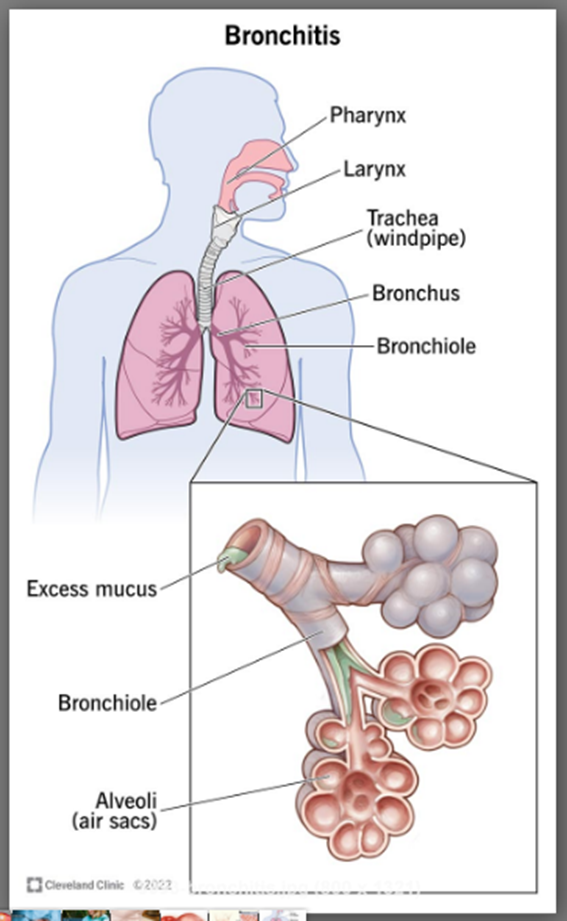
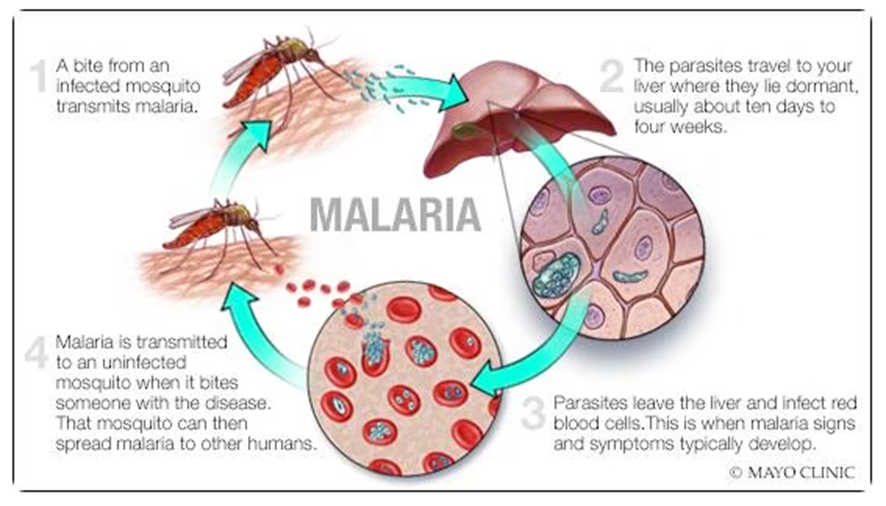
6. Malaria
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of malaria may include:
7. Influenza
Flu, also called influenza, is an infection of the nose, throat and lungs, which are part of the respiratory system. The flu is caused by a virus. Influenza is commonly called the flu, but it's different from the stomach "flu" viruses that cause diarrhea and vomiting.
Other symptoms include:
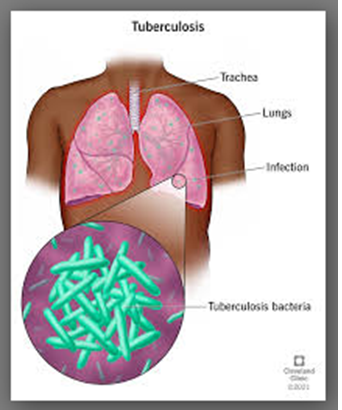
8. Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious illness that mainly affects the lungs. The germs that cause tuberculosis are a type of bacteria.
Symptoms of active TB disease in the lungs usually begin gradually and worsen over a few weeks. They may include:
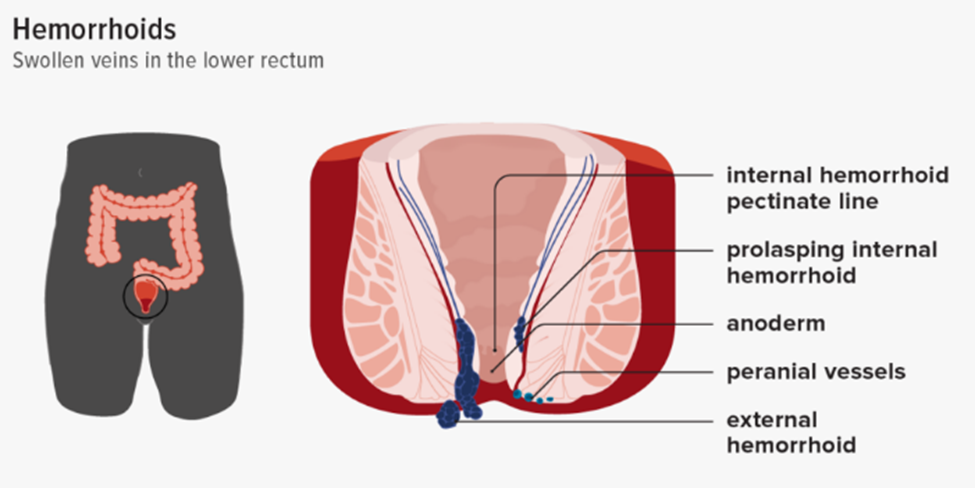
9. Hemorrhoids / Piles
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins in the lower part of the anus and rectum. When the walls of these vessels stretch, they can become irritated. Older age, pregnancy, and constipation can cause piles.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids often include:
10. Scabies
Scabies is caused by the Sarcoptes scarbiei mite. It causes a rash so itchy that it interrupts sleep. It can be treated with certain ointments or pills.
Scabies is a skin condition caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis mite. These little bugs make tunnels (burrow) under your skin and cause small red bumps and severe itching. Scabies spreads easily from person to person, especially among people who live close together. If one family member has scabies, a provider should check and treat other family members and close contacts at the same time.
Symptoms of scabies include:
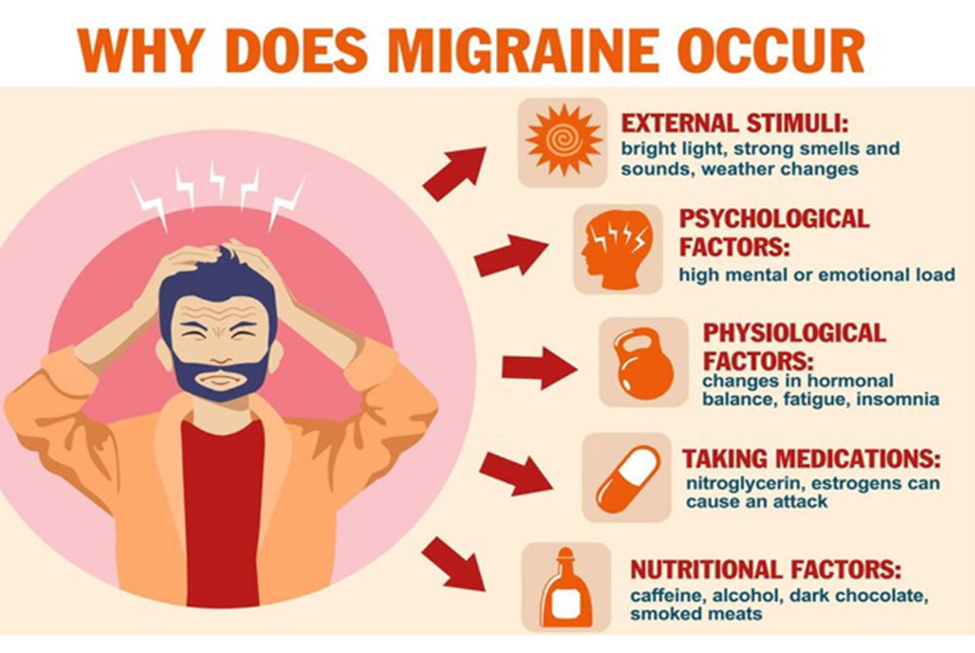
11. Migraine / Headache
A migraine is much more than a bad headache. It can cause debilitating, throbbing, one-sided head pain that can leave you in bed for days. Movement, lights, sounds and other triggers may cause symptoms like fatigue, nausea, vision changes, irritability and more. A healthcare provider can help you manage symptoms so migraines don't take over your life.
A migraine is a severe headache that causes throbbing, pulsing head pain on one side of your head. The headache phase of a migraine usually lasts at least four hours, but it can also last for days. This headache gets worse with :-
Physical activity
Bright lights
Loud noises
Strong odors
One or two days before a migraine, you might notice subtle changes that warn of an upcoming migraine, including:
migraine auras include:
Attack
A migraine usually lasts from 4 to 72 hours if untreated. How often migraines occur varies from person to person. Migraines might occur rarely or strike several times a month.
During a migraine, you might have:
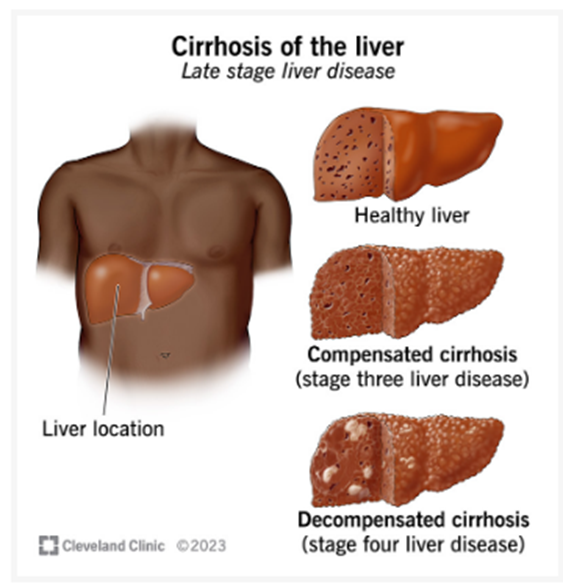
12. Cirrhosis of the liver
Cirrhosis of the liver is permanent scarring that damages your liver and interferes with its functioning. It can lead to liver failure. Cirrhosis is the result of persistent liver damage over many years. Alcohol and drugs, viruses and metabolic factors are the most common causes.
Cirrhosis of the liver is late stage liver Disease in which healthy liver tissue has been gradually replaced with scar tissue. This is a result of long-term, chronic hepatitis. Hepatitis is inflammation in your liver, which has many causes. When inflammation is ongoing, your liver attempts to repair itself by scarring. But too much scar tissue prevents your liver from working properly. The end stage is chronic Liver Failure.
Early signs and symptoms of cirrhosis may include:
13. Hernia
A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For example, the intestines may break through a weakened area in the abdominal wall.
Many hernias occur in the abdomen between your chest and hips, but they can also appear in the upper thigh and groin areas.
Most hernias aren't immediately life threatening, but they don't go away on their own. Sometimes they can require surgery to prevent dangerous complications.
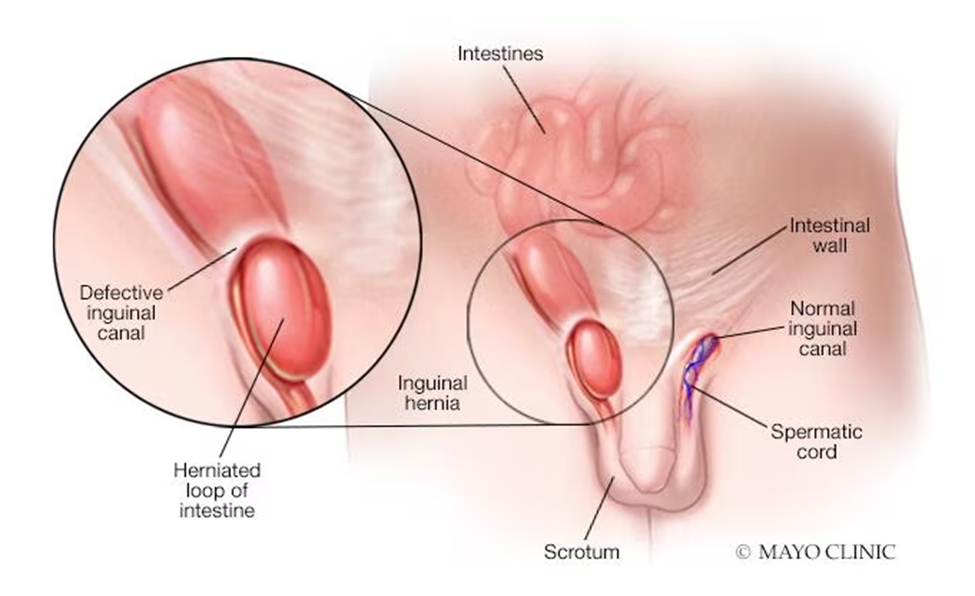
Inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernia. They occur when the intestines push through a weak spot or tear in the lower abdominal wall, often in the inguinal canal.
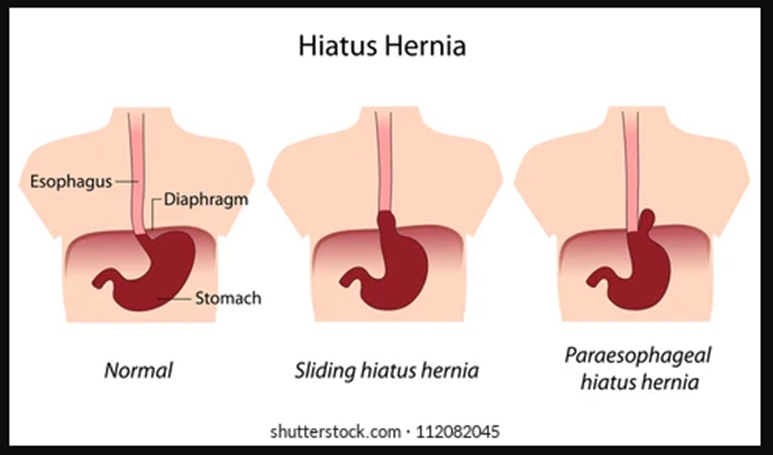
Hiatal hernia
A hiatal hernia occurs when part of your stomach protrudes up through the diaphragm into your chest cavity. The diaphragm is a sheet of muscle that helps you breathe by contracting and drawing air into the lungs. It separates the organs in your abdomen from those in your chest.
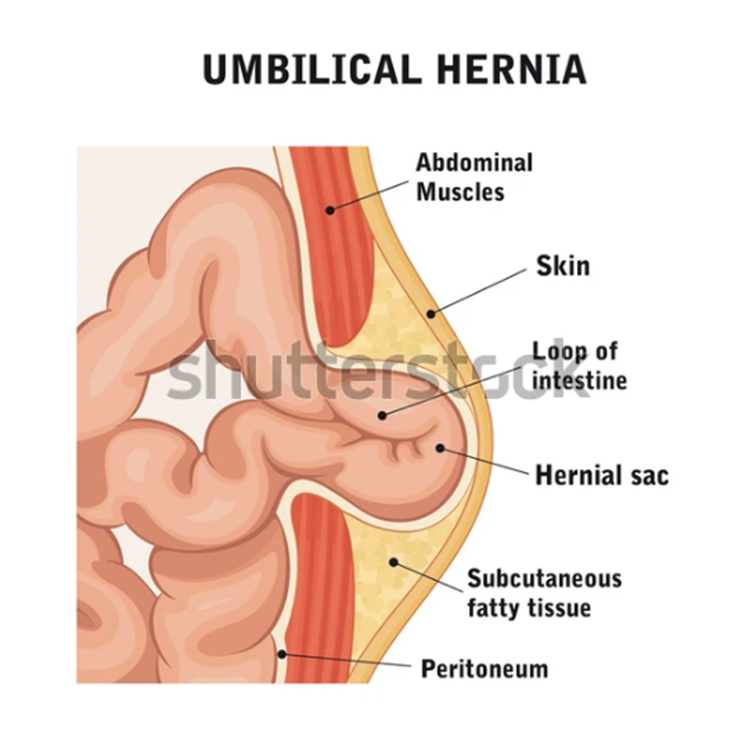
Umbilical hernia
Umbilical hernias can affect children and babies. They occur when the intestines bulge through the abdominal wall near the belly button. You may notice a bulge in or near your child's belly button, especially when they're crying.
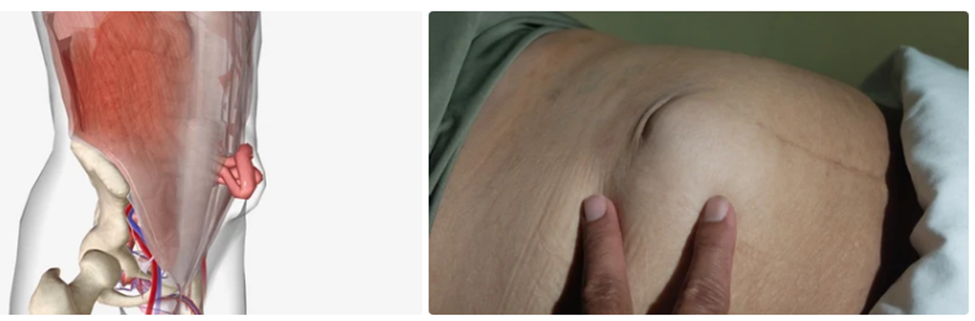
Ventral hernia
A ventral hernia happens when tissue bulges through an opening in the muscles of your abdomen. You may notice that a ventral hernia decreases in size when you're lying down.
Hernia signs and symptoms include:
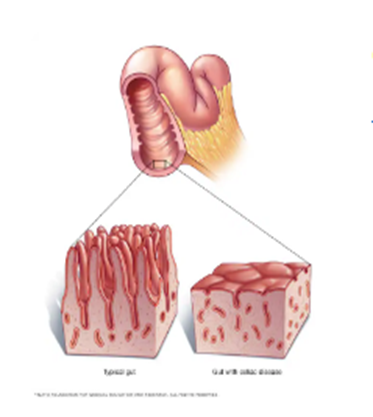
14. Celiac disease
Celiac disease is an illness caused by an immune reaction to eating gluten. Gluten is a protein found in foods containing wheat, barley or rye.
If you have celiac disease, eating gluten triggers an immune response to the gluten protein in your small intestine. Over time, this reaction damages your small intestine's lining and prevents it from absorbing nutrients, a condition called malabsorption.
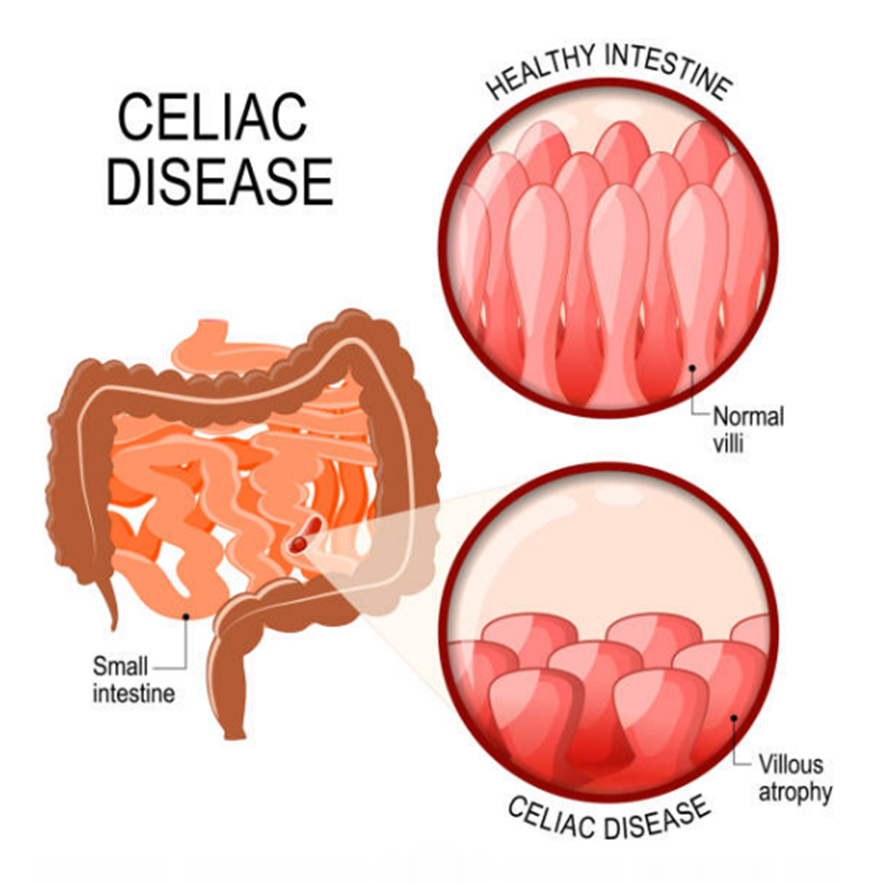
Symptoms
The symptoms of celiac disease can vary greatly. They also may be different in children and adults. Digestive symptoms for adults include:
However, more than half the adults with celiac disease have symptoms that are not related to the digestive system, including:
Children
Children with celiac disease are more likely than adults to have digestive problems, including:
The inability to absorb nutrients might result in:
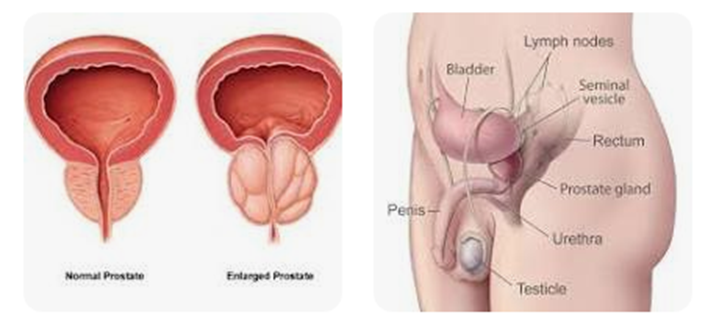
15. Prostate Diseases
The symptoms of prostate problems include:
Other symptoms depend on the type of prostate problem you have and may include:
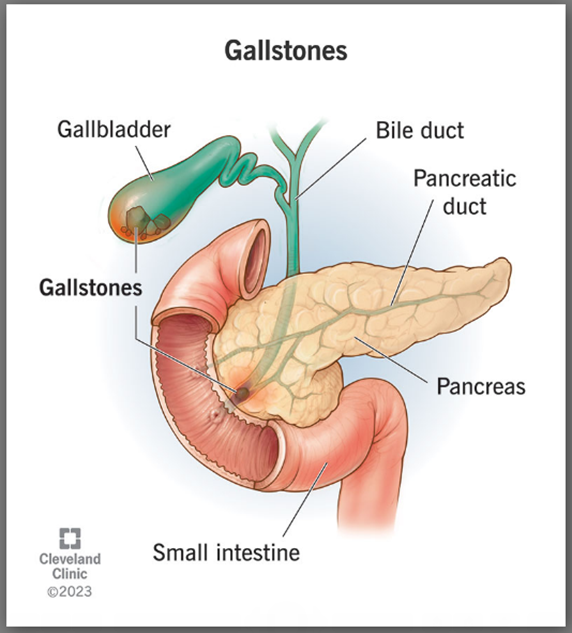
16. Cholelithiasis / Gallstones
Gallstones are hardened, concentrated pieces of bile that form in your gallbladder or bile ducts. "Gall" means bile, so gallstones are bile stones. Your gallbladder is your bile bladder. It holds and stores bile for later use. Your liver makes bile, and your bile ducts carry it to the different organs in your biliary track.
Healthcare providers sometimes use the term "cholelithiasis" to describe the condition of having gallstones. "Chole" also means bile, and "lithiasis" means stones forming. Gallstones form when bile sediment collects and crystallizes. Often, the sediment is an excess of one of the main ingredients in bile.
Gallstones generally don't cause symptoms unless they get stuck and create a blockage. This blockage causes symptoms, most commonly upper abdominal pain and nausea. These may come and go, or they may come and stay. You might develop other symptoms if the blockage is severe or lasts a long time, like:-
Sweating
Fever
Fast heart rate
Abdominal swelling and tenderness
Yellow tint to your skin and eyes
Dark-colored pee and light-colored poop
17. Renal calculi
Renal calculi; Nephrolithiasis; Stones - kidney; Calcium oxalate - stones; Cystine - stones; Struvite - stones; Uric acid - stones; Urinary lithiasis.
Kidney stones are common. Some types run in families. They often occur in premature infants.
There are different types of kidney stones. The cause of the problem depends on the type of stone.
Stones can form when urine contains too much of certain substances that form crystals. These crystals can develop into stones over weeks or months.
Calcium stones can also form from combining with phosphate or carbonate.
Other types of stones include:
The main symptom is severe pain that starts and stops suddenly:
Symptoms can include:
18. Prostate stones
Prostate stones are small calcium deposits in the prostate that are very common in men from middle-age onwards, but are usually harmless. If they cause pain or problems when urinating, they can be treated.
At a glance
19. Sinusitis
The sinuses are small air pockets located in between the eyes and behind the forehead, nose, and cheekbones. When the sinuses and nasal passages become inflamed, it's known as sinusitis.
Inflammation can occur because of conditions such as structural issues in the nose or a sinus infection. The terms "sinusitis" and "sinus infection" are sometimes used interchangeably.
A sinus infection is a very common condition. According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, sinus infections affect 31 million people in the United States each year.
Sinusitis symptoms
The symptoms of sinusitis are similar to those of a common cold. They may include:
It may be difficult for caregivers to detect sinusitis in a child. Signs include:
Need a Doctor for Check-up?
Copyright © 2018 DR. MIRZA'S HOMOEO | All Rights Reserved